Spin flip
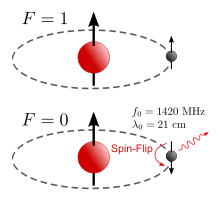
Hydrogen in the ground state , with magnetically parallel (F = 1) and antiparallel (F = 0) setting of the electron ( hyperfine structure ). The spin-flip transition releases an amount of energy that corresponds to a frequency of 1420 MHz. Because of the associated wavelength of 21 cm, the radiation is also called the 21 cm line (alternatively: hydrogen line, HI line).
In physics , a spin-flip is the realignment (especially the reversal) of the spin of a particle , such as an electron .
However, one speaks of a spin flip in the narrower sense only when an energy barrier has to be overcome. This is e.g. This is the case, for example, with a particle in a magnetic field , because then the energy degeneration of the various spin states is usually eliminated. If the magnetic field is very strong, thermally excited spin flips are completely suppressed.