Radiation length
The radiation length is a characteristic length for the energy loss due to radiation when charged particles pass through matter. It is a material-specific constant that is usually specified as a mass allocation. In addition, the radiation length is linked to the mean free path of high-energy photons.
Energy loss of charged particles
Charged particles can lose energy in several ways. These include losses due to ionization or the emission of radiation. The radiation length only refers to the energy loss due to radiation, which predominates with light particles and high energies. The limit from which radiation losses dominate is called critical energy. It is defined as the energy at which losses due to ionization and radiation are the same and is material-dependent. The ionization losses are described using the Bethe formula .
Radiation losses
Radiation losses occur due to the interaction of charged particles with electromagnetic fields. There are different types of radiation, such as B. bremsstrahlung , transition radiation , synchrotron radiation or Cherenkov radiation . For light particles, bremsstrahlung is particularly important because the radiated power is proportional to . An acceleration when passing through matter is caused by scattering z. B. caused by cores.
The energy loss due to radiation is also described. Where is the radiation length. The generated photons usually have enough energy to create new particles through pairing . This creates an electromagnetic particle shower .
Free path of photons
The interaction of high-energy photons with matter is dominated by pair formation. The mean free path of a high-energy photon is linked to the radiation length of a material. It applies to the mean free path .
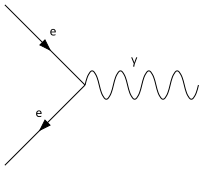
The fact that the radiation length is characteristic of the energy loss due to radiation from charged particles as well as of photons can be seen by looking at the corresponding Feynman diagrams for the two dominant processes. Since both cases are about the same vertex, only "rotated", a similar behavior can be expected. The corresponding vertex is shown here, a rotation of approx. 45 ° corresponds to the generation of bremsstrahlung, a rotation of 180 ° results in the vertex for pair generation.
meaning
Since the radiation length is characteristic of the energy loss of charged particles as well as of photons, it defines a length scale for electromagnetic showers. This is particularly important for the construction of calorimeters in particle physics or for radiation therapy with light particles or photons. This is also important for dimensioning shields.
For the calculation of the radiation lengths there are approximate formulas that depend on the atomic number Z. Values for certain materials are also tabulated.
literature
- Wei-Ming Yao et al. (Particle Data Group): 2006 Review of Particle Physics . In: J. Phys. G. 33, 2006 ( Section 27.4 ).