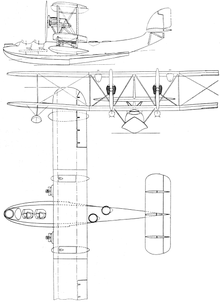
Supermarine Southampton
| Supermarine Southampton | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Type: | Flying boat |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
March 10, 1925 |
| Commissioning: |
1925 |
| Production time: |
1925-1933 |
| Number of pieces: |
83 |
The Supermarine Southampton was a very successful during the period between the two World Wars British biplane - flying boat .
history
The development was based on the Supermarine Swan , which was a flying boat for ten passengers and was used between England and France. The Southampton was designed by the later designer of the Supermarine Spitfire , Reginald J. Mitchell . Due to the success of the Swan, six Southampton were ordered straight from the drawing board, very unusual for the Royal Air Force (RAF). The development time from the Swan was very short. The first flight of Southampton took place on March 10, 1925. As early as mid-1925, the six machines were delivered to the RAF.
Further machines were sold abroad, eight machines to Argentina , one each to Australia and Turkey . In Japan, a Southampton was later converted into an 18-seat passenger aircraft. One machine (G-AASH) flew for Imperial Airways .
A total of 83 Southampton and one Southampton X with three engines were built.
construction
The Southampton was a twin-engine, biplane flying boat. The type Mk I still had a fuselage and wings made of wood. The Mk II already had a metal hull made of duralumin . This machine was 409 kg lighter and could therefore fly 325 km further. In 1929 all Mk I were fitted with metal hulls. The Mk III finally got wings made of duralumin.
The machine had three machine gun positions, one in the aircraft nose and two in the rear fuselage.
production
Approval of the Supermarine Southampton by the RAF:
| version | 1925 | 1926 | 1927 | 1928 | 1929 | 1930 | 1931 | 1932 | 1933 | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mk.I | 6th | 18th | 24 | |||||||
| Mk.II | 7th | 20th | 5 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 40 | |||
| Mk.II enclosed cockpit | 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| total | 6th | 18th | 7th | 20th | 0 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 4th | 66 |
Engine variants
- Mk I - Napier Lion V
- Mk II - Napier Lion Va
- Argentine Mk I - Lorraine 12E
- Turkish Mk I - Hispano-Suiza 12 Nbr
- Experimentally also Bristol Jupiter IX and Rolls-Royce Kestrel
Military use
Technical specifications
| Parameter | Data |
|---|---|
| crew | 4th |
| length | 15.15 m |
| span | 22.86 m |
| height | 6.20 m |
| Wing area | 134.5 m² |
| Empty mass | 4398 kg |
| Takeoff mass | 6895 kg |
| drive | two Napier Lion Va with 500 PS (368 kW) each |
| Top speed | 153 km / h at sea level |
| Service ceiling | 6160 m |
| Range | 1223 km |
| Armament | three 7.7 mm MG, max. 500 kg bombs |
See also
literature
- Charles Ferdinand Andrews, Eric B. Morgan: Supermarine aircraft since 1914 . Putnam, 1987, ISBN 978-0-85177-800-6 (399 pages).
Web links
- Supermarine Southampton. In: Royal Air Force Museum London. Retrieved June 19, 2009 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Halley, James J .: The K File. The Royal Air Force of the 1930s , Tunbridge Wells, 1995, p. 322; Thompson, Dennis: Royal Air Force Aircraft J1 – J9999 , Tonbridge 1987