Windows Performance Index
The Windows Performance Index ( English Windows Experience Index (WEI) ) is a module from Windows Vista, 7, 8 and 10, which provides information on the performance of the individual components and the overall system of a personal computer ( benchmark software ) using a point scale .
The function should help the user to evaluate the performance of his system. Originally, a user should also be able to recognize whether a software with a required performance figure assigned by the manufacturer runs on a given system. In addition, it should be easier to see for which hardware component the upgrade makes sense.
Under Vista, the function can be called up by pressing the Windows and Pause buttons at the same time, or via the control panel under “Performance information and tools”.
As of Windows 8.1, the performance index can no longer be calculated or displayed via the user interface, but only via the command line program WinSAT ( Windows System Assessment Tool ), which must be executed as an administrator in the command line:
winsat formal
The result is saved as an XML file in:
%windir%\Performance\WinSAT\DataStore\
in a file with the name Formal.Assessment (Recent) .WinSAT.xml and a date and time specification .
On the basis of the evaluation, programs determine the available scope of performance, issue warning messages or refuse to install, so there are also programs to manipulate the index.
construction
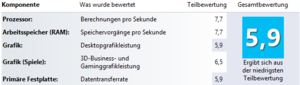
The index shows the performance of the individual computer components such as processor , memory , graphics card and hard drive and can also be dependent on the software installed, such as updates to the operating system. The results of the test are shown as numerical values. In Vista, the performance scale ranges from 1.0 (lowest score, low performance) to 5.9 (maximum score, high performance), in Windows 7 from 1.0 to 7.9, and in Windows 8 and Windows 10 from 1.0 to 9.9. The overall rating of computer performance is derived from the lowest partial rating. Particularly low results can indicate obsolete hardware or computer problems (e.g. defective hardware or missing / incorrect device drivers ).
software
- hWinSAT - shows the WEI in the usual form, including history
- Create performance index determine under Windows 10 (Microsoft Store)
Web link
Individual evidence
- ↑ Axel Vahldiek: Microsoft celebrates the launch of Windows Vista. heise online, January 29, 2007, accessed on May 25, 2013 .
- ↑ Christof Windeck: SSD and SuperFetch. c't , January 2012, accessed May 25, 2013 .
- ↑ Performance Index Manipulator. screenzocker13.eu, March 3, 2012, accessed May 25, 2013 .
- ↑ Your computer's Windows Performance Index Score may change after you install Windows Vista Service Pack 1. Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved May 25, 2013 .