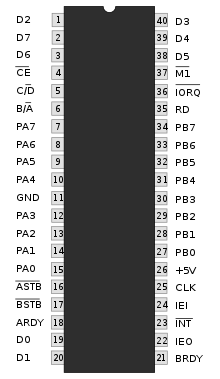
Z80 PIO
The parallel input / output ( PIO ) interface of the Z80 family organizes the parallel data transfer between the microcomputer and the peripherals . The activities of the PIO circuit are controlled exclusively by the CPU . It is therefore necessary that both circuits can exchange signals with one another.
Since a processor is responsible for several peripheral devices, it also receives several interrupt signals, but can only process one per time unit. Prioritization must therefore be guaranteed. The interrupt requestor (= the device requesting the interrupt) must signal to the system both the beginning and the end of its CPU usage. Several PIOs can be prioritized among one another by daisy- chaining via the IEI-IEO connections.
- IEI (= Interrupt-Enable In): PIO is authorized to send interrupt vector / INT to the CPU if no PIO with a higher priority sends an interrupt.
- IEO (= Interrupt-Enable Out): Interrupt is processed, PIOs with lower priority must wait.
Operating modes:
- Mode 0 : Byte-wise output
- Mode 1 : Byte-wise input
- Mode 2 : Bidirectional input and output
- Mode 3 : single bit control (for bit-parallel output of control signals)