Sande (Friesland)
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 53 ° 30 ' N , 8 ° 1' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Lower Saxony | |
| County : | Friesland | |
| Height : | 2 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 44.87 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 8792 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 196 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 26452 | |
| Primaries : | 04422, 04421 | |
| License plate : | FRI | |
| Community key : | 03 4 55 014 | |
| LOCODE : | DE SDE | |
| Community structure: | 5 districts | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Hauptstrasse 79 26452 Sande |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Stephan Eiklenborg ( independent ) | |
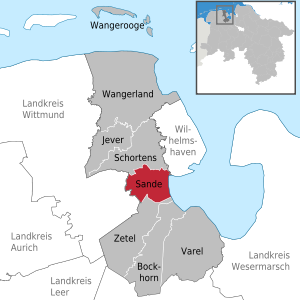
| Location of the municipality of Sande in the district of Friesland | ||

Sande is a municipality in the district of Friesland , Lower Saxony (Germany).
geography
"In the middle of Friesland - life between the Geest and the sea" is how the municipality of Sande fits in geographically. It is located on the edge of the Jeverland and ten kilometers south of the North Sea city of Wilhelmshaven .
Neighboring communities
The municipality of Sande borders the city of Schortens in the north, the independent city of Wilhelmshaven in the northeast , the municipality of Zetel in the south and the municipality of Friedeburg in the west .
Community structure
The municipality of Sande consists of the five districts of Sande, Neustadtgödens , Cäciliengroden , Mariensiel and Dykhausen .
The area of the former municipality of Gödens - Altgödens, Dykhausen, Gödens and Neustadtgödens - has belonged to the municipality of Sande and thus to the district of Friesland since the municipality reform of 1972. Before these places belonged to the district of Wittmund , that is, to East Frisia . The church reform had no effect on the affiliation of the churches located in Gödens.
Land use
Around 80% of the community area consists of forest and agricultural areas. The building and open spaces account for around 10%. The total other land use can be seen in the following table:
| Land use in 2006 | Area in ha |
|---|---|
| Buildings and open spaces | 415.01 |
| Traffic areas | 321.40 |
| Operating areas | 3.46 |
| Forest and agricultural areas | 3546.26 |
| Bodies of water | 103.00 |
| Recreational areas | 39.74 |
| Other areas | 58.34 |
| total area | 4487.21 |
climate
Sande is located in a temperate climate zone that is directly influenced by the North Sea . According to the Köppen climate classification , the municipality is in the Cfb division . C stands for a warm-temperate climate, fb for a humid-temperate climate with summers in which the daytime temperatures are lower and winters in which the daytime temperatures are often higher than in the further inland. Overall, the climate is shaped by the Central European west wind zone.
history

Until the early Middle Ages , the area between the Geest and the coast, in which the municipality is now also located, was transformed into a fertile marshland by sand . As early as 400 to 800 AD there were numerous Frisian sausages and terps , some of which are still preserved today. From around 900 AD, villages and individual farms secured their fields from storm surges with ring dikes . Related dikes were built in the 13th century. At that time, the flood hazard for sands did not yet come from the jade in the east, but from the Maade Bay in the north. It was not until the 14th century that the Jade Bay expanded massively, so that after the Antoni flood in 1511, Sande and Gödens formed a peninsula, at first probably even an island, in the Black Brack .
The oldest source for the mention of Sande comes from the year 1168. The districts that belong to Sande today are of significantly different ages: Altgödens is mentioned as early as 785, while the development of Dykhausen in 1175 roughly coincides with that of Sande. Neustadtgödens is only mentioned after the end of the Middle Ages around 1544, Mariensiel around 1570 and Cäciliengroden not until 1938. In the Middle Ages, the parish Seediek was located in the municipality, which was abandoned in 1511 after the Antoni flood.
From the 15th to the 19th century there was the glory of Gödens in the west of today's municipal area , which turned away from the rule of Jever in 1495 and subordinated the county of East Friesland , whose history it shared until the dissolution of the administrative district of Aurich .
The construction of the Ems-Jade Canal and the expansion of Wilhelmshaven as an imperial naval base at the end of the 19th century brought an economic upswing for Sande with improved infrastructure (e.g. rail links).
The Nazi plans for the Wilhelmshaven economic area served to expand it into the "City of 500,000" as the largest location for Hitler's navy and as an armaments factory. The Sanderbusch settlement had already begun during the Weimar Republic. According to the 1937 economic plan, u. a. a southern town of Sande for 25,000 inhabitants will be built. Chief planner Wilhelm Hallbauer envisaged the "residential area Wilhelmshaven Süd" with Sanderbusch, Sande, Gödens and Cäciliengroden in the 1939 economic plan. Only the Cäciliengroden settlement (1938–39) was built for 360 families by Wilhelmshaven shipyard workers. The client was the Jade housing association, an architect from Bremen's Friedrich Heuer, a typical representative of Heimatschutz architecture and the National Socialist settlement ideology. Parts of the planned industrial area east of the new Reichsstrasse 69 were also built, such as the foundry of the Kriegsmarine shipyard, the North German ironworks and the militarily important Sande train station. For the workers of the industrial area and the Wilhelmshavener Westwerft, the shipyard workers town of Sande-Neufeld was built between 1939 and 1940 for 3,600 (mostly foreign) shipyard workers, which was only to be converted into people's apartments for families after the war. The development plan came from Karl Tuchscherer. The architect of the spartan, simple and cheap warehouse city was the general planner Fritz Hilgenstock from Hanover. During the Nazi era, there were also significant naval structures in and around Sande. The naval hospital Sanderbusch hospital (1937–39) was built by Kurt Geisenhainer from the naval construction department for 600 beds. Mention should also be made of the neighboring Roffhausen marine equipment store (1937), later Olympia-Werke. Since Sande had facilities essential to the war effort, a large bunker was built near the station. Occasionally there was bomb damage from Allied aircraft.
In 1933 Sande was incorporated into the new municipality of Oestringen , but was regained its municipal independence in 1948. Due to the favorable transport connections , some companies settled in the following period, later mainly in the newly created industrial area Bahnhofstraße / Weserstraße / Elektronikring.
Incorporations
On July 1, 1972, the municipality of Gödens was incorporated into the municipality of Sande through an administrative reform. This doubled the area to 45 km 2 . Initially made considerations for the expansion of the community area by adding areas of the neighboring community Zetel were ultimately not carried out.
Population development
The population development in the municipality of Sande is shown in the following table:
|
politics
Municipal council
The municipality council of the municipality of Sande consists of 22 councilors. This is the specified number for a municipality with a population between 8001 and 9000 inhabitants. The 22 council members are elected for five years each by local elections. The current term of office began on November 1, 2016 and ends on October 31, 2021.
The full-time mayor Stephan Eiklenborg is also entitled to vote in the local council.
The last local election on September 11, 2016 resulted in the following:
| Political party | Proportional votes | Number of seats | Change voices | Change seats |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPD | 64.01% | 14th | −0.73% | −1 |
| CDU | 19.48% | 4th | −1.41% | −1 |
| Alliance 90 / The Greens | 11.75% | 2 | −1.48% | −1 |
| FDP | 4.01% | 2 | + 3.63% | +1 |
The turnout in the 2016 local elections was 56.41%, slightly above the Lower Saxony average of 55.5%. For comparison - in the previous municipal election on September 11, 2011, the turnout was 52.65%.
In the constituent council meeting on November 2, 2016, the SPD councilwoman Ulrike Schlieper was elected as the new council chairwoman. Her deputy was Michael Ramke from the SPD. Michael Ramke and Ruth Bohlke (both SPD) were unanimously elected as honorary mayors.
mayor
The full-time mayor of the municipality of Sande has been the non-party individual applicant Stephan Eiklenborg since 2014. In the last mayoral election on May 25, 2014, he ran against the previous incumbent Josef Wesselmann. Eiklenborg won the election with 57.41% of the vote, his opponent Wesselmann received 42.58%. The turnout was 54.27%. Eiklenborg took office on November 1, 2014.
Representatives in the Land and Bundestag
In the elections to the Lower Saxony state parliament , Sande belongs to the state electoral district 070 Friesland , which includes the entire district of Friesland. The direct mandate was won on October 15, 2017 by Olaf Lies from the SPD. On November 22, 2017, Lies was elected Minister for the Environment, Energy, Building and Climate Protection of Lower Saxony. The electoral term ends in 2022.
Sande belongs to the parliamentary constituency Friesland - Wilhelmshaven - Wittmund . It includes the city of Wilhelmshaven and the districts of Friesland and Wittmund . The directly elected MP is Siemtje Möller (SPD). No party candidate from the constituency entered the Bundestag via the parties' list.
coat of arms
The coat of arms of the municipality of Sande is split . The right side of the coat of arms shows the Marienturm of the former castle in Altmarienhausen, which was built by Miss Maria von Jever on the Marienhausen estate. The Jeverland lion is shown on the left , as Sande belonged to the Jever rule for centuries . The three wave symbols are supposed to indicate the proximity to the sea.
Partnerships
The municipality of Sande has had a partnership with the West Pomeranian city of Ueckermünde since June 15, 2007 .
The first contacts between the communities of Ueckermünde and Sande were made shortly after the fall of the Wall through letters from local sports clubs. On 17./18. January 1990 the mayor of Ueckermündes and the deputy chairman of the sports club of the city of Ueckermünde visited Sande, already on the 24th and 25th. January 1990 the first return visit was made by a delegation from a Sander sports club. Since then, intensive contacts have been maintained at various levels, which led to the official declaration of the partnership with the exchange of certificates in 2007.
Culture and sights
- The Sander landmark : the Marienturm of the former castle (1568–1571)
- St. Magnus Church in Sande (14th century) - The church is the oldest building in Sande.
- Coastum - Coastal Protection Exhibition in Sande-Altmarienhausen
- Gödens Castle (1517) - A previous building of today's castle burned down in 1669. Harro Burchard von Frydag had the moated castle built in its current form in 1671 . In 1746 Gödens came into the possession of the von Wedel family through marriage. The exterior is in the style of the Dutch Renaissance . The ceiling-high, picturesque decoration of the state hall with representations from Greek mythology is worth seeing . The castle, which is still inhabited today, can only be partially visited during events. The palace park, on the other hand, is freely accessible. The entrance gate to the castle park has some inscriptions from 1653.
- Wedelfeld water pumping mill (1844)
- Museum in the Landrichterhaus Neustadtgödens (16th century)
- Former synagogue in Neustadtgödens
- Oberahmer Peldemühle in Neustadtgödens / Sanderahm (1764)
- Sculpture path art on the dike on the sea dike to the Jade Bay between Mariensiel and Dangast ( EXPO 2000 project in Cäciliengroden)
- Friesischer Heerweg - At 400 km, it is the longest continuously signposted cycling route in East Friesland
Sports
Sande owns with the Gemeindesportbund Sande e. V. (GSB Sande) the only community sports association in Lower Saxony. It was founded in 1969 as an amalgamation of all Sander gymnastics and sports clubs and serves to represent the interests of municipalities, businesses and the owner and operator of the sports hall "Klaus-Bünting-Halle".
- Klootschießer- und Boßelverein Cäciliengroden (KBV "Hart um Hart")
- Klootschießer- und Boßelverein Neustadtgödens (KBV "Fleu herut")
- Klootschießer- und Boßelverein Freesenspeel Sande (KBV Freesenspeel)
- Klootschießer- und Boßelverein Dykhausen (KBV "Lütt End")
- Gymnastics and Sports Club Sande from 1863 (TuS Sande)
- Gymnastics and Sports Club Cäciliengroden (TuS Cäci)
- Sandhoppers squash club
- Canoe and Sailing Club Sande (KSV Sande)
- Sanderbusch tennis club
- Game Association Gödens (SV Gödens)
- Sande shooting club
- Gödens shooting club
- FFC Sande 90 e. V. (recreational soccer)
- FC Rot-Weiß Sande / Cäciliengroden
- "Monte Pinnow" climbing bunker of the German Alpine Club, Wilhelmshaven section
- Leisure facility Sander See - The Sander See was created in the course of motorway construction work.
- ECW Sande e. V. "The Jadehaie" ( Ice Hockey Regional League North)
- SV Gödens Vikings (Ice Hockey National League North)
- Sande ice rink
- Sande paddle and pedal station - here you can borrow canoes or bicycles. The handover is possible in Friedeburg and Sande at the respective station.
Regular events
From the event calendar of the municipality of Sande, the following regular events with great regional awareness are worth mentioning:
- May: Landpartie Schloss Gödens - Country-style exhibition on the grounds of the moated castle in Gödens
- July: Sander market - large folk festival in the center of Sande
- August: Settler Festival Cäciliengroden - event of the settler communities I. and II.
- November: Terp plaster - on the occasion of the inspection of the first-order trenches by the Weser-Ems water and soil association
- in summer: North German climbing championships - at the bunker ruins at Sande train station (German Alpine Association)
Economy and Infrastructure
traffic
Road links
The municipality of Sande has a direct connection to the federal motorway 29 , which leads from Wilhelmshaven via Oldenburg to the Ahlhorner Heide motorway triangle . From the Sande junction of the A 29, the federal road 436 (short: B 436) leads via Friedeburg , Wiesmoor across East Friesland and to Weener near the Dutch border. Sande is also connected to the town of Schortens via the K 294 and branching off from it via a feeder to the federal road 210 north of Sande , which leads via Jever and Wittmund to Aurich.
Rail connections
Sande is located on two railway lines and has the “Sande” train station and the “Sanderbusch” stop in the middle of the village (on the route towards Jever). The first connection, the Wilhelmshaven – Oldenburg railway ( timetable KBS 392), runs from Wilhelmshaven via Sande to Oldenburg . The NordWestBahn travels the subsequent route in the direction of Osnabrück via Cloppenburg . There are also connections to Bremen and Hanover , mostly you have to change trains in Oldenburg. From October 2011 to January 2013, the Wilhelmshaven – Oldenburg line was expanded to connect the JadeWeserPort in Wilhelmshaven to two tracks. Therefore, the route between Sande and Rastede was closed to passenger traffic for a long time. As an alternative, a replacement bus service was operated on the blocked connection.
Another connection is the East Frisian Coast Railway (RB 59). This line runs on the route Wilhelmshaven Hbf - Sande - Schortens - Jever - Wittmund - Esens and is also operated by the NordWestBahn every hour. The journeys are carried out on behalf of the LNVG , the tariff of the transport association Ems-Jade (VEJ) applies .
Freight traffic to the Wilhelmshaven industrial areas on the Voslapper and Rüstersieler Groden is also handled via the single-track section Sande – Sanderbusch . In connection with the construction of the JadeWeserPort, a strong increase in traffic is expected. Therefore, a railway bypass is currently under construction, which should lead around Sande in a north-easterly direction. The previous route and the Sanderbusch stop will be canceled.
Since 2011, on the occasion of the weekend on the Jade, the southern route of the former Wilhelmshaven suburban railway from Sande station to the Pumpwerk cultural center in Wilhelmshaven has been used by the so-called "Sande Express". This is a shuttle service with a Uerdingen rail bus from the former " Hümmlinger Kreisbahn ".
Waterways
The Ems-Jade Canal , which connects the Ems near Emden in East Friesland with the Jade Bay near Wilhelmshaven , runs past Sande . It is administered by the Lower Saxony State Office for Water Management, Coastal Protection and Nature Conservation in Aurich . The Ems-Jade Canal is 72.3 km long and, ascending from the Ems in Emden, passes the towns of Ihlow , Südbrookmerland and Aurich, and then descends via Wiesmoor , Reepsholt , Sande to Wilhelmshaven to the Jade Bay . The canal has six locks and is crossed by 15 fixed and 26 movable bridges. It is only navigable for ships up to 33 m long, 6.20 m wide and 1.70 m deep and has therefore been used almost exclusively for tourism for some time.
Wilhelmshaven-Mariensiel airfield
The Wilhelmshaven-Mariensiel regional airfield , which is operated jointly by the district of Friesland and the city of Wilhelmshaven, is located in the municipality . The airfield is mainly used for sport flights. On request, flights to the North and East Frisian Islands also depart from there.
Established businesses
The nationwide best-known company in Sande is the electronics shipping company Reichelt Elektronik . After Conrad Electronic, the mail order company is the second largest private customer electronics mail order company in Germany. In addition, the foundry "Sande Stahlguss GmbH" and "NE Sander Eisenbau GmbH", a subsidiary of Ed. Züblin AG , based. The central traffic management of WIKING Helikopter Service GmbH is located at the Wilhelmshaven-Mariensiel airfield . The company carries out the maritime pilot transfer service in the German Bight on behalf of the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure . Wiking also works together with the emergency command .
media
The Wilhelmshavener Zeitung , the Jeversche Wochenblatt and the Nordwest-Zeitung report on topics from Sande every working day.
In December 2007, the Frisian Broadcasting Corporation moved to Sande and was initially located in the buildings of the former Klein printing house. In 2010 the FRF moved into the former community center. In January 2018 the FRF left Sande and moved to Friedeburg .
Public facilities
The Sanderbusch Northwest Hospital is located in Sande . The hospital employs around 750 people and is of great economic importance as the municipality's largest employer. The hospital provides standard care and has a total of 384 beds. The district of Friesland is responsible for the facility.
The Northwest Hospital covers the departments of internal medicine , general surgery , neurosurgery , trauma surgery , orthopedics , neurology , anesthesiology and intensive care medicine from. Around 12,000 inpatients and around 8,000 outpatients are cared for in the hospital every year . Since 1982, the hospital is also the site of the ADAC - rescue helicopter "Christoph 26". An MBB / Kawasaki BK 117 is currently in service. The rescue helicopter is responsible for the entire Weser-Ems region including the East Frisian Islands . The hospital is affiliated with the University of Göttingen as an academic teaching hospital and serves to train young students in the medical faculty . The collaboration with the university gives the hospital direct access to the latest medical procedures and treatment methods.
education
The following schools exist in the municipality:
- Sande Elementary School
- Elementary school Neustadtgödens
- Cäciliengroden primary school
- Sande High School
The next general high school in the Friesland district is the Mariengymnasium in Jever, about twelve kilometers away, with a branch in Schortens. The grammar schools in the neighboring city of Wilhelmshaven are closer and easier to reach, but because of the different school districts they are not allowed to be attended by Sander pupils. The Cecilia School in Wilhelmshaven is an exception , as it is run by the church. The Fachgymnasien in Wilhelmshaven can be visited, provided that there is no comparable offer at the vocational schools in Jever.
Personalities
Sons and daughters of the church
- Albert Brahms (1692–1758), dike and hydraulic engineering specialist
- Carl Wilhelm Jaspers (1850–1940), politician, father of the philosopher Karl Jaspers
- Olga Potthast von Minden (1869–1942), painter
- Wilhelm Schlegtendal (1906–1994), architect
- Konrad Ehrensberger (1936–2009), naval officer, most recently flotilla admiral of the German Navy
- Hans-Jörg Oestern (* 1945), trauma surgeon
- Peter Behrens (1947–2016), drummer
- Michael Konken (* 1953), journalist
- Olaf Kühl (* 1955), Slavist
- Ulrich Becker (* 1960), lawyer and university lecturer
- Gorch Pieken (* 1961), military historian
- Hans-Georg Bohlken (* 1962), European champion in toilet shooting
- Jens Hübschen (* 1972), radio and television presenter
- Arne Tammen (* 1972), soccer player
Personalities associated with Sande
- Johann Conrad Koch († 1803 in Sande), teacher and organist in Sande, great-great-grandfather of the chemist, entrepreneur and billionaire Fred Chase Koch
- Ludwig Schauenburg (1839–1909), pastor and church historian
literature
- Hans Egidius: The black brackish - a region asserts itself against the forces of nature. The geographical and historical development of the western Jadebusen from Mariensiel to Varel. CCV, Varel 1999, ISBN 3-934606-00-8 .
- Ingo Sommer : The city of 500,000. Nazi urban planning and architecture in Wilhelmshaven. Vieweg Braunschweig / Wiesbaden, Braunschweig / Wiesbaden 1993, ISBN 3-528-08851-6 , pp. 82 ff., 109 ff., 133 ff., 150 ff.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ State Office for Statistics Lower Saxony, LSN-Online regional database, Table 12411: Update of the population, as of December 31, 2019 ( help ).
- ↑ Citizens' information brochure of the municipality of Sande, page 7 (PDF; 9.7 MB) ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b Citizens' information brochure of the municipality of Sande, page 12 (PDF; 9.7 MB) ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Citizens' information brochure of the municipality of Sande, page 6 (PDF; 9.7 MB) ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer GmbH, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 275 .
- ↑ NLA OL Rep 400 Order 138 No. 158 - Reclassification of a sub-area ... - Arcinsys detail page. Retrieved December 18, 2017 .
- ^ Lower Saxony Municipal Constitutional Law (NKomVG) in the version of December 17, 2010; Section 46 - Number of MPs , accessed on November 2, 2016
- ↑ a b Municipality of Sande - overall results of the 2016 municipal council election , accessed on November 4, 2016
- ↑ The CDU gets the most votes nationwide. September 12, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2016 .
- ↑ Wilhelmshavener Zeitung of November 3, 2016: “Quickly into the new electoral period”, page 11
- ↑ Sande: Stephan Eiklenborg wins mayoral election , accessed on 22 October 2014
- ↑ Olaf Lies: About me , accessed on June 20, 2013
- ↑ Allocation of constituencies to the Federal Returning Officer , accessed on August 17, 2019.
- ^ Nordwest-Zeitung: Bundestag election: These members represent our region . In: NWZonline . ( nwzonline.de [accessed September 29, 2017]).
- ↑ http://kirche-sande.de/
- ↑ Gödens Castle in the Northwest Travel Magazine
- ↑ ECW Sands
- ↑ 2018 || Senior National League Group A - Ice Hockey in the Northern Association. Accessed March 7, 2019 (German).
- ↑ Sande ice rink
- ↑ Sande paddle and pedal station
- ↑ Two-track expansion to connect the Jade-Weser-Port has started , accessed on December 4, 2011
- ↑ Train route blocked until the end of 2012 due to connection to deep water port , accessed on December 4, 2011
- ↑ Planning approval procedure for the laying of the Sande railway ( memento of January 11, 2013 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ Overview map of the planned railway relocation ( memento from February 17, 2013 in the web archive archive.today ).
- ↑ DB Netze railway laying Sande accessed on January 3, 2020.
- ^ NWZ-Online, December 10, 2007: Friesischer Rundfunk moves to Sande , accessed on October 13, 2015.
- ↑ NWZ-Online, February 16, 2009: The station starts in the community center , accessed on October 13, 2015.
- ^ Family tree: Johann Conrad Koch → Harry Koch (father of Fred C. Koch) , accessed on February 25, 2016.