Superior gluteal artery: Difference between revisions
integrated picture |
m →Superficial branch: +links |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Superficial branch== |
==Superficial branch== |
||
The superficial branch enters the deep surface of the [[ |
The superficial branch enters the deep surface of the [[glutæus maximus]], and divides into numerous branches, some of which supply the muscle and anastomose with the [[inferior gluteal artery]], while others perforate its tendinous origin, and supply the integument covering the posterior surface of the sacrum, anastomosing with the posterior branches of the [[lateral sacral arteries]]. |
||
==Deep branch== |
==Deep branch== |
||
Revision as of 19:05, 17 October 2007
| Superior gluteal artery | |
|---|---|
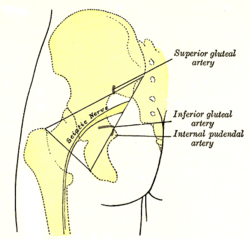 Left gluteal region, showing surface markings for arteries and sciatic nerve. | |
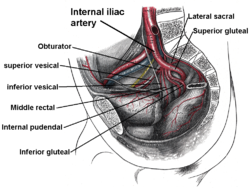 Internal iliac artery and some of its branches. Superior gluteal artery labeled at right | |
| Details | |
| Source | Internal iliac artery |
| Vein | Superior gluteal veins |
| Supplies | Gluteus maximus muscle, Piriformis muscle, Tensor fasciae latae |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria glutea superior |
| TA98 | A12.2.15.013 |
| TA2 | 4310 |
| FMA | 18868 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The superior gluteal artery (gluteal artery) is the largest branch of the internal iliac artery, and appears to be the continuation of the posterior division of that vessel.
It is a short artery which runs backward between the lumbosacral trunk and the first sacral nerve, and, passing out of the pelvis above the upper border of the Piriformis, immediately divides into a superficial and a deep branch.
Within the pelvis it gives off a few branches to the Iliacus, Piriformis, and Obturator internus, and just previous to quitting that cavity, a nutrient artery which enters the ilium.
Superficial branch
The superficial branch enters the deep surface of the glutæus maximus, and divides into numerous branches, some of which supply the muscle and anastomose with the inferior gluteal artery, while others perforate its tendinous origin, and supply the integument covering the posterior surface of the sacrum, anastomosing with the posterior branches of the lateral sacral arteries.
Deep branch
The deep branch lies under the Glutæus medius and almost immediately subdivides into two.
Of these, the superior division, continuing the original course of the vessel, passes along the upper border of the Glutæus minimus to the anterior superior spine of the ilium, anastomosing with the deep iliac circumflex artery and the ascending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex artery.
The inferior division crosses the Glutæus minimus obliquely to the greater trochanter, distributing branches to the Glutæi and anastomoses with the lateral femoral circumflex artery.
Some branches pierce the Glutæus minimus and supply the hip-joint.
See also
Additional images
-
Left Levator ani from within.
-
The arteries of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions.
-
Dissection of side wall of pelvis showing sacral and pudendal plexuses.
External links
- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Anatomy photo:43:13-0105 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: Branches of Internal Iliac Artery"
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 622 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 622 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)