Saponification
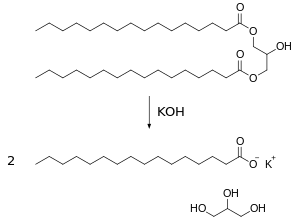

Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester under basic conditions to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid. Saponification is commonly used to refer to the reaction of a metallic alkali (base) with a fat or oil to form soap. Saponifiable substances are those that can be converted into soap.
both heated →
- CH2-OH -CH-OH - CH2-OH (glycerol) + 3 R-CO2-Na (soap)
- where R=(CH2)14CH3 in the example (right)
Lye is a form of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) which is a caustic base. If NaOH is used a hard soap is formed, whereas a soft soap is formed when potassium hydroxide (KOH) is used.
Vegetable oils and animal fats are fatty esters in the form of triglycerides. The alkali breaks the ester bond and releases the fatty acid and glycerol.
The soap is salted out by precipitating it with saturated sodium chloride.
Saponification in corpses
Saponification can also refer to the conversion of fat and other soft tissue in a corpse into adipocere, often called "grave wax." This process is more common where the amount of fatty tissue is high, the agents of decomposition absent or only minutely present, and the burial ground is particularly alkaline.
Saponification in fire extinguishers
Fires involving cooking fats and oils should be extinguished with a wet chemical extinguisher. Extinguishers of this type are designed to extinguish cooking fats and oils through saponification. The extinguishing agent rapidly converts the burning substance to a non-combustible soap. This process is endothermic, meaning it absorbs energy (in this case, thermal energy) from its surroundings, eliminating the fire and decreasing the temperature.
See also
External links
- Soapmaking at Bellaonline - Soapmaking articles, forum and supplier links.
- Soap Naturally Web and Mailing List - Resources for natural handmade soapmakers.
- Soap Recipe Corner - Soapmaking explained.
- About Candle and Soap Making - Soap making at About.com
- Glossary for the Modern Soap Maker - A collection of terms, definitions and acronyms for today's soap maker.
- Adipocere - A collection of resources on soap mummies and adipocere formation.
