Ugaritic alphabet
| Ugaritic | |
|---|---|
| Script type | |
Time period | from around 1500 BC |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| Languages | Ugaritic, Hurrian |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Ugar (040), Ugaritic |
| Unicode | |
Unicode alias | Ugaritic |
The Ugaritic alphabet is a cuneiform abjad (alphabet without vowels), used from around 1500 BC for the Ugaritic language, an extinct Canaanite language discovered in Ugarit, Syria. It has 31 distinct letters. Other languages (particularly Hurrian) were occasionally written in it in the Ugarit area, although not elsewhere.
Clay tablets written in Ugaritic provide the earliest evidence of both the Levantine and South Semitic orders of the alphabet, which gave rise to the alphabetic orders of the Hebrew, Greek, and Latin alphabets on the one hand, and of the Ge'ez alphabet on the other.
The script was written from left to right.
Origin
Scholars have searched in vain for cuneiform prototypes of the letters of the Ugaritic alphabet. However, recently some have come to the conclusion that Ugaritic may have been a form of the Semitic alphabet,[1] the letter forms distorted as an adaptation to writing on clay with a stylus.
For example, the two basic shapes in cuneiform, a linear wedge, as in 𐎂, and a corner wedge, as in 𐎓, may correspond to lines and circles in the linear Semitic alphabets: the three Semitic letters with circles, preserved in the Greek Θ, O and Latin Q, are all made with corner wedges in Ugaritic: 𐎉 Tet, 𐎓 Ain, and 𐎖 Qopa. Other letters look similar as well: 𐎅 Ho resembles its assumed Greek cognate E, while 𐎆 Wo, 𐎔 Pu, and 𐎘 Thanna are similar to Greek Y, Π, and Σ turned on their sides.[2]
Abecedaries
Lists of Ugaritic letters have been found in two alphabetic orders: the "Northern Semitic order" more similar to the one found in the Hebrew and Phoenician, and more distantly, the Greek and Latin alphabets; and the "Southern Semitic order" more similar to the one found in the South Arabian, and more distantly, the Ge'ez alphabets. The letters are given in transcription and in their Hebrew cognates; letters missing from Hebrew are left blank.
North Semitic
| ’a | b | g | x | d | h | w | z | ħ | ṭ | y | k | š | š' | l | m | ð | n | ẓ | s | c | p | ṣ | q | r | θ | γ | t | ś | ’i | ’u |
| א | ב | ג | ח׳ | ד | ה | ו | ז | ח | ט | י | כ | ל | מ | ד׳ | נ | ט׳ | ס | ע | פ | צ | ק | ר | ש | ע׳ | ת | שׂ |
South Semitic
| h | l | ħ | m | q | w | š | r | t | s | k | n | x | b | ś | p | ’ | c | ẓ | g | d | γ | ṭ | z | ð | y | θ | ṣ |
| ה | ל | ח | מ | ק | ו | ר | ת | ס | כ | נ | ח׳ | ב | שׂ | פ | א | ע | ט׳ | ג | ד | ע׳ | ט | ז | ד׳ | י | ש | צ |
Special Characters
Letters
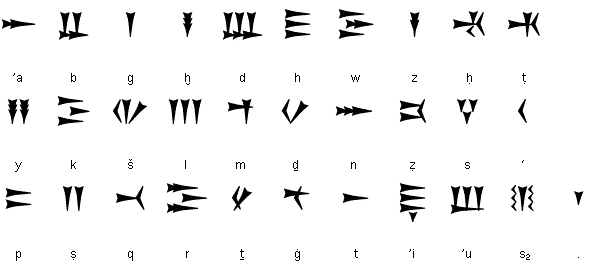
| 𐎀 | ʾa | alpa |
| 𐎁 | b | beta |
| 𐎂 | g | gamla |
| 𐎃 | ẖ | ẖa |
| 𐎄 | d | delta |
| 𐎅 | h | ho |
| 𐎆 | w | wo |
| 𐎇 | z | zeta |
| 𐎈 | ḥ | ḥota |
| 𐎉 | ṭ | ṭet |
| 𐎊 | y | yod |
| 𐎋 | k | kaf |
| 𐎌 | š | šin |
| | š2 | šinš |
| 𐎍 | l | lamda |
| 𐎎 | m | mem |
| 𐎟 | ḏ | ḏal |
| 𐎐 | n | nun |
| 𐎑 | ẓ | ẓu |
| 𐎒 | s | samka |
| 𐎓 | ʿ | ʿain |
| 𐎔 | p | pu |
| 𐎕 | ṣ | ṣade |
| 𐎖 | q | qopa |
| 𐎗 | r | raša |
| 𐎘 | ṯ | ṯanna |
| 𐎙 | ġ | ġain |
| 𐎚 | t | to |
| 𐎝 | s2 | śu |
| 𐎛 | ʾi | i |
| 𐎜 | ʾu | u |
| 𐎟 | word divider | |
Ugaritic in Unicode
In Unicode, the Ugaritic alphabet is assigned to U+10380 - U+1039F.
| Ugaritic[1][2] Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+1038x | 𐎀 | 𐎁 | 𐎂 | 𐎃 | 𐎄 | 𐎅 | 𐎆 | 𐎇 | 𐎈 | 𐎉 | 𐎊 | 𐎋 | 𐎌 | 𐎍 | 𐎎 | 𐎏 |
| U+1039x | 𐎐 | 𐎑 | 𐎒 | 𐎓 | 𐎔 | 𐎕 | 𐎖 | 𐎗 | 𐎘 | 𐎙 | 𐎚 | 𐎛 | 𐎜 | 𐎝 | 𐎟 | |
| Notes | ||||||||||||||||
External links
- Ugaritic writing
- Ugaritic script (ancientscripts.com)
- Ugaritic cuneiform Omniglot entry on the subject
- Download an ugaritic font (uncludes Unicode font)
- Ugaritic cuneiform characters from the Unicode Ugaritic cuneiform script
- Ugaritic script (Brian Colless - version 1)
- Ugaritic script (Brian Colless - version 2)
