Matairesinol: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
added chembl id |
Updating {{chembox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or [[user talk |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{chembox |
{{chembox |
||
| Verifiedfields = changed |
|||
| verifiedrevid = 400294983 |
| verifiedrevid = 400294983 |
||
| Reference = <ref>[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/ProductDetail.do?lang=en&N4=40043|FLUKA&N5=SEARCH_CONCAT_PNO|BRAND_KEY&F=SPEC Matairesinol] at [[Sigma-Aldrich]]</ref> |
| Reference = <ref>[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/ProductDetail.do?lang=en&N4=40043|FLUKA&N5=SEARCH_CONCAT_PNO|BRAND_KEY&F=SPEC Matairesinol] at [[Sigma-Aldrich]]</ref> |
||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
| CASOther = |
| CASOther = |
||
| PubChem = 119205 |
| PubChem = 119205 |
||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} |
|||
| ChEMBL = 425148 |
| ChEMBL = 425148 |
||
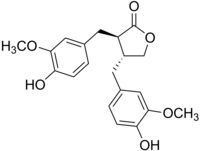
| SMILES = O=C2OC[C@H](Cc1cc(OC)c(O)cc1)[C@H]2Cc3ccc(O)c(OC)c3 |
| SMILES = O=C2OC[C@H](Cc1cc(OC)c(O)cc1)[C@H]2Cc3ccc(O)c(OC)c3 |
||
Revision as of 15:37, 1 August 2011
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3R,4R)-3,4-bis[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]oxolan-2-one
| |
| Other names
(αR,βR)-α,β-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)butyrolactone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H22O6 | |
| Molar mass | 358.390 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Matairesinol is a plant lignan. It occurs with secoisolariciresinol in numerous foods such as oil seeds, whole grains, vegetables, and fruits.[2]
The plant lignans are precursors of the enterolignans (mammalian lignans). A number of plant lignans are metabolized to the enterolignans (enterodiol and enterolactone) that can potentially reduce the risk of certain cancers and cardiovascular diseases.[3]
Although there are studies which indicate the disease prevention (cardio-protective and hormone associated cancers like breast cancer) benefits of lignans, the results are not yet conclusive. [4]
References
- ^ Matairesinol at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Niemeyer HB, Honig DM, Kulling SE, Metzler M (2003). "Studies on the metabolism of the plant lignans secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol". J. Agric. Food Chem. 51 (21): 6317–25. doi:10.1021/jf030263n. PMID 14518962.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Milder IE, Arts IC, van de Putte B, Venema DP, Hollman PC (2005). "Lignan contents of Dutch plant foods: a database including lariciresinol, pinoresinol, secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol". Br. J. Nutr. 93 (3): 393–402. doi:10.1079/BJN20051371. PMID 15877880.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University
