Acetate: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
Rifleman 82 (talk | contribs) Revert to revision 162842160 dated 2007-10-07 10:53:47 by Rifleman 82 using popups |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
--> |
--> |
||
The cow goes moo |
|||
==Notation in organic chemistry== |
|||
In the field of [[organic chemistry]] the abbreviation ''Ac'' refers to the [[acetyl]] group. Hence, acetate can be written '''<sup>−</sup>OAc''' or '''AcO<sup>−</sup>''' and [[acetic acid]], [[sodium acetate]], and [[ethyl acetate]] can be denoted by HOAc, NaOAc, and EtOAc respectively. |
|||
Ac is also the symbol for the [[chemical element]] [[actinium]], but confusion between actinium and the acetyl group is rare, since actinium has virtually no role in organic chemistry. |
|||
== no == |
|||
moo moo moo moo |
|||
==Structures== |
==Structures== |
||
Revision as of 18:40, 18 October 2007
An acetate, or ethanoate, is a salt or ester of acetic acid.
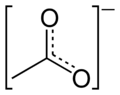
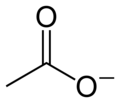
Acetate anion
The acetate anion, [C2H3O2]−, is a carboxylate and is the conjugate base of acetic acid. The acetate ion is formed by the deprotonation of acetic acid:
- CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO− + H+
Acetate esters
An acetate ester is an ester of acetic acid, with the general formula C2H3O2R, where R is an organyl group.
Acetate can also refer to cellulose acetate, especially fibres or other derived products such as the acetate disc used in audio record production. Cellulose acetate can be found in many household products.
The cow goes moo
no
moo moo moo moo
Structures
-
space-filling model of the acetate anion -
ball-and-stick model of the acetate anion -
structural formula of the acetate anion -
resonance hybrid of the acetate anion -
canonical forms of the acetate anion -
skeletal formula of the acetate anion -
general skeletal structure of an acetate ester -
skeletal structure of the acetyl group
See also
Wikimedia Commons has media related to acetates.