Adaga
| Adaga | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Information | |
| Weapon type: | Parrying weapon |
| Designations: | Adaga, Adarga, Adargue, El-Darakah |
| Region of origin / author: |
Arabia , ethnic groups in Arabia |
| Distribution: | Arabia, India |
| Handle: | Wood, metal |
| Lists on the subject | |
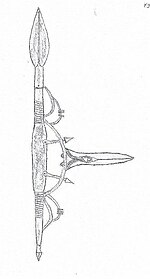
The Adaga (Spanish for dagger), also Adarga, Adargue, Adargue or arab. el-Darakah (derived from shield) is a parrying weapon developed in Arabia, intended for defense and attack (English Parrying Weapon).
description
The Adaga consists of a kind of short spear that serves as a handle. The spear has a leaf-shaped, double-edged spear blade on one side and a short blade on the other. The short shaft of the spear serves as a handle . A large metal bracket is attached to the center of the spear and two smaller ones to the right and left of it. The middle bracket is covered with leather. It serves as a shield and hand protection when using the Adaga with one hand. The two smaller temples serve as hand protection when used with both hands. In the middle of the large handle is a long, double-edged dagger blade, which is used to attack the enemy. The Adaga described here should not be confused with the Spanish-Moorish shield Adaga . The adaga was used in Arabia.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ George Cameron Stone, Donald J. LaRocca: A Glossary of the Construction, Decoration and Use of Arms and Armor: in All Countries and in All Times. Courier Dover Publications, 1999, ISBN 978-0-486-40726-5 (reprint).
literature
- George Cameron Stone , Donald J. LaRocca: A Glossary of the Construction, Decoration and Use of Arms and Armor: in All Countries and in All Times. Courier Dover Publications, 1999, ISBN 978-0-486-40726-5 (reprint).
- Richard Francis Burton : The book of the sword. 1884, Dover Publications, 1987, ISBN 978-0-486-25434-0 (reprint), pages 12, 281.