Ameloblastoma
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| D16 | Benign neoplasm of bone and articular cartilage |
| D16.4 | Bones of the cranial and facial skull maxilla |
| D16.5 | Lower jaw |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
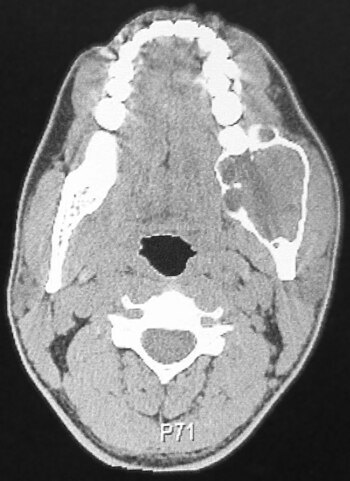
The ameloblastoma (from Old English amel "enamel" and ancient Greek βλάστη blastä "germ") (outdated: adamantinoma) is a locally invasively growing tumor that is derived from the enamel- forming cells, the ameloblasts .
pathology
The ( odontogenic ) tumors emanating from the teeth are derived from the embryonic tooth system. This consists of mesodermal and ectodermal parts (see cotyledon ). The ameloblastoma shows a frequent tendency to recurrence and is usually benign, i.e. H. it does not metastasize . Malignant ameloblastoma is rare ; it can arise from a pre-existing benign ameloblastoma or develop de novo . A distinction is made between the tubular ( follicular ) type and the reticulated ( plexiform ) type.
clinic
The ameloblastoma is usually an incidental finding that appears as a painless jaw expansion. About 30% of ameloblastomas arise from follicular cysts . In later stages it can change the position of the teeth through resorption processes and cause sensitivity disorders through displacement and pressure on nerves. It is found in the lower jaw (preferred places: jaw angle and ascending lower jaw branch) six times more frequently than in the upper jaw (canine region). Mostly younger patients (30–40 years of age) are affected, although the distribution is roughly the same for men and women.
diagnosis
Diagnosis is only possible through a histological examination of the cyst-like follicle. Radiological evidence can be the fact that neoplastic events are more prone to tooth resorptions. However, tooth resorptions can rarely occur in normal odontogenic cysts .
Imaging procedures
The x-ray shows a one (soap bubble-like) or multi-chambered (honeycomb-like), sharply delimited lightening with dissolution of the cortex due to bone dissolution ( osteolysis ).
Differential diagnosis
- radicular cyst at the tip of the root, emerges from Mallassez's epithelial remains
- follicular cyst on the lower jaw, rarely transition to ameloblastoma
- odontogenic keratocyst (formerly: keratocystic odontogenic tumor)
- odontogenic squamous cell tumor
- calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (Pindborg tumor)
- ameloblastic fibroma
- ameloblastic fibroodontoma
- ameloblastic fibrodentinoma
- Odontoameloblastoma
- Giant cell granuloma
- Osteosarcoma
therapy
The therapy of choice consists of resection safely in healthy individuals with a safety margin of 5 mm and the subsequent primary bone reconstruction. From a prognostic point of view, a restoration of the previous state is to be expected postoperatively, but due to the tendency to recurrence, (semi) annual checks over a period of 5 to 10 years are recommended.
literature
- N. Schwenzer, M. Ehrenfeld: Dental, oral and maxillofacial medicine . 2010
- H.-P. Howaldt, R. Schmelzeisen: Introduction to oral and maxillofacial surgery . 2002
- Pschyrembel . 257th edition.
- Riede, Schäfer: Pathology . 3. Edition.
- A new face for Tsehaye . (PDF; 74 kB) In: Bayerisches Zahnärzteblatt , 10/2010
Web links
- Macroscopic image on Patho Pic
- Metastatic ameloblastoma. ZM-online
Individual evidence
- ^ Walter Hoffmann-Axthelm : Lexicon of dentistry . Quintessenz-Verlag, Berlin
- ↑ Merva Soluk-tekkesin, John M. Wright: The world health organization classification of odontogenic lesions: a summary of the changes of the 2017 (4th) edition . In: Turkish Journal of Pathology . 2013, ISSN 1018-5615 , doi : 10.5146 / tjpath.2017.01410 ( turkjpath.org [accessed November 14, 2018]).
Note: The term ameloblastoma is an etymological bastard .