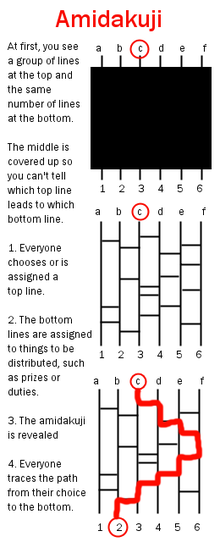
Amida-kuji
Amida-kuji ( Japanese 阿 弥陀 籤 or あ み だ く じ ' Amitabha -Los', Chinese 畫 鬼 腳 / 画 鬼 脚 , Pinyin hua gui jiao - "drawn ghost feet " or 鬼 腳 圖 / 鬼 脚 图 , gui jiao tu - "ghost picture " ) is the Japanese name of a raffle form known in Asia , in which a certain number of participants are given a corresponding number of prizes.
The basis for the raffle is an initially unknown graph consisting of vertical lines. The number of vertical lines is equal to the number of participants. Horizontal connections (bridges) can exist between adjacent vertical lines. Each participant is assigned an upper end of such a line. Each lower end is linked to a price. After the assignment, the graph becomes visible.
Now each participant follows his line downwards. When reaching each bridge, this must be followed. After all, each participant reaches a certain price at the low end.
In addition to the parallel arrangement of the vertical lines in the shape of a staircase, they can also depart from a center at equal angles, the connections then forming concentric circles and the graph resembling a spider's web. Based on this form of representation in connection with the use of the lottery for charitable purposes, the Japanese name is also derived, as the network is reminiscent of the wreath of light from the Buddha Amitābha.
Math background
If the participants and prizes are numbered consecutively, then an Amida-kuji can mathematically be viewed as a permutation of the numbers from to . This ensures that
- not two participants receive the same price and
- each prize is assigned to a participant.
The number of horizontal lines added does not matter.
In addition, if there is a sufficient number of horizontal lines, each participant can receive any prize, regardless of the order of the participants and the prizes.
Amida-kujis work for any number of participants, as long as there are that many prizes.
literature
- Man-Kit Ho, Hoi-Kwan Lau, Ting-Fai Man, Shek Yeung: Ghost Leg . In: Hang Lung Mathematics Awards Collection of Winning Papers, 2004 . International Press, 2012, ISBN 978-1-57146-254-1 .