anamorphic
The adjective anamorphic ( pronunciation : [ anaˈmɔrf ], correspondingly “redesigned” from Greek: ana “up”, “on”; morphae “form, shape”) describes the distorted state of an image compared to the original. The term “ anamorphic ”, which can also mean the distorting property of an optical system, is also used in technical optics .
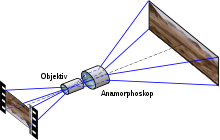
Usually an anamorphic image is created with a cylinder lens or a cylinder mirror (distorting mirror). The distorted image (more rarely the process of distortion or rectification) is called anamorphosis . A lens (or lens attachment) that images anamorphically is called anamorphic .

Anamorphic utilization of the film material by Cinemascope
|
Applications
Effect or perspective compensation
In the Renaissance was anamorphic painting a popular stylistic device. Pictures were painted in such a way that they could only be recognized undistorted after the illustration through an anamorphic lens. Rather unnoticed, anamorphosis was also used to make paintings on vaulted ceilings appear undistorted to the viewer. A very similar application can be found today with traffic signs that are drawn on the road surface with strong longitudinal distortions so that they appear proportionate to the driver despite the very flat viewing angle.
Film technology
With the anamorphic process in film technology, the principle of the anamorphic image was again widely used from the 1950s onwards to accommodate wide-screen formats on normal-format carriers without losing unused film surfaces.
Digital video technology
Somewhat misleading, it is also called anamorphic image recording in digital image storage when non-square pixels are used. Misleading because in the digital state one cannot actually speak of a geometrical-optical distortion; this only arises when the anamorphic pixels are incorrectly displayed as a square.
literature
- Joost Elffers, Mike Schuyt, Fred Leeman: Anamorphoses. A game with perception, appearances and reality (= DuMont pocket books. Vol. 107). DuMont, Cologne 1981, ISBN 3-7701-1300-4 .