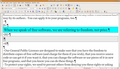
Anaphraseus
| Anaphraseus
|
|
|---|---|
 Anaphraseus 2.04.98b on macOS |
|
| Basic data
|
|
| developer | Oleg Tsygani, Dmitri Gabinsky and Sergei Medvedev |
| Current version | 2.08 (December 23, 2019) |
| operating system | Windows , Linux , Mac OS X , Solaris , FreeBSD and other Unix flavors |
| programming language | StarOffice Basic |
| category | Computer Aided Translation (CAT) |
| License | GPL ( Free Software ) |
| anaphraseus.sf.net | |
Anaphraseus is a computer-aided translation (CAT) program in the form of a free extension for OpenOffice.org Writer . It was largely inspired by Wordfast , a proprietary CAT program for Microsoft Word , and consists of a collection of macros written in StarOffice Basic . Anaphraseus has been developed under the GNU GPL license since October 2007 by a group of independent translators and programmers .
functionality
The user opens the document to be translated in OpenOffice.org Writer and select the translation memory (Engl. Translation memory, TM ) from which he wants to use. If he does not have a TM available, he can create a new one. The TM file format used by the software is the Wordfast format. It is also possible to import a TM in the standardized TMX format. However, importing in this way can take a relatively long time: To make this process easier, it is advisable to use the free Okapi Olifant conversion software . In addition, Anaphraseus offers the option of integrating one or more glossaries (word lists, terminological collections).
The translation process runs linearly from one segment (usually a sentence) to the next. If a new segment is opened, the software makes a translation proposal to the user: the translation unit stored in the TM with the highest degree of similarity to the segment just opened. The user is free to accept, reject or adapt this translation suggestion. At the same time, the software automatically looks up the terms in the currently opened segment in the existing glossary (s). After the translation of the segment has been completed (e.g. by navigating to the next segment), the text entered by the user is automatically saved in the TM and the segment in the source language is placed in the background.
Once the translation of the document has been completed, the user has a bilingual file: the source segments are in the background, the target segments in the foreground (similar to after using Wordfast or Trados Translator's Workbench ). The last step is the « clean-up » (removal of the original segments from the document), which is carried out by clicking on the corresponding menu item. The user can of course use the translation memory that has been "expanded" by new segments for further projects.
Overview of the functionalities
Functionalities already implemented
- Translation memory
- Exact and fuzzy matches
- Glossaries
Planned functionalities
- Search within the TM (concordance search)
- Analysis of the source and target text material
- Merging TMs
Screenshots
literature
- Oleg Tsygany: "Anaphraseus: translators' workhorse". Panace @. Vol. 10, No. 29, pp. 58–60: http://www.tremedica.org/panacea/IndiceGeneral/n29_tribuna-Tsygany.pdf (en) ( Permalink )