Base station controller
The Base Station Controller ( BSC ; German base station controller ) is a network element of the digital GSM - the mobile radio network .
General
Several base stations (BTS, "Base Transceiver Station") are connected to the Base Station Controller . The connection between a base station and the higher-level Base Station Controller is known as the A-bis-Link . Mostly these are implemented as 2 Mbit PCM lines. Base station controller, base stations and transcoder (TRC) together form the Base Station Subsystem (BSS).
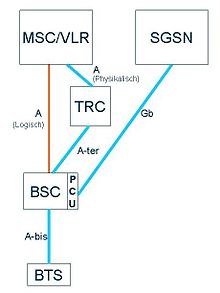
Several base station subsystems are connected to a Mobile Services Switching Center (MSC) via so-called A-Links . Telephony and circuit-switched data traffic are handled via the MSC . For packet-switched data traffic ( GPRS ), on the other hand, the Base Station Controllers are connected to a Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) via a Gb connection .
Tasks of the Base Station Controller
The base station controller monitors the radio connections in the GSM network and, if necessary, initiates power control and cell changes ( handover ). If the old and new base stations are connected to the same base station controller during a handover, the controller carries out the handover independently, otherwise the higher-level MSC is involved.
In order to obtain a basis for decision-making for power control and handover, level and quality measurements are carried out by the mobile station and base station and the measurement results are communicated to the base station controller.
Interfaces
A-bis interface
The A bis interface between the base station and the base station controller divides 64 kbit / s channels into several subchannels, since the voice information in the cellular network is encoded with a lower bit rate . The signaling is carried out according to the LAPD protocol of the ISDN signaling DSS1 . As a rule, manufacturers also use their own protocols for Operation and Maintenance (O&M), so that the A-bis interface is at least partially proprietary . See also: Operation and Maintenance Center
A-ter interface
Via the A-ter interface between the base station controller and the transcoder, the base station controller requests the encoding of a 64 kbit / s channel according to a specific codec . The GSM codecs are standardized for FR phase 1 (full rate), FR phase 2 (enhanced full rate), FR phase 3 (AMR full rate), as well as HR phase 1 (half rate) and HR phase 3 (AMR half rate). In the event that the preferred codec is not available in the transcoder, the Base Station Controller gives a list of possible codecs. The A-ter interface is usually proprietary, so it is usually not possible to connect base station controllers and transcoders from different manufacturers.
A interface
The A interface to the MSC corresponds to a 2 Mbit / s transmission system PCM30 with 30 user channels and one signaling channel. However, SDH (155 Mbit / s STM-1 ) is also used to reduce the need for multiplexers . The signaling protocol is part of the Signaling System 7 . The A interface is very well standardized so that mobile switching centers and base station controllers from different manufacturers can work together. The A-ter interface is logically the direct connection to the MSC, but physically mostly runs via the transcoder, which in turn has no logical connection to the MSC.
Gb interface
The Gb interface connects the Base Station Controller with the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) and is used for IP -based services . The Packet Control Unit (PCU) in the Base Station Controller is used for this . Either Ethernet or Frame Relay via 2 Mbit / s PCM cables is used as the transmission technology .