Cellulose acetate propionate
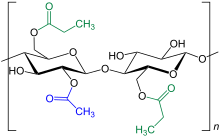
Schematic (simplified) formula presentation from the polymer chain of cellulose acetate propionate with an acetyl radical ( marked in blue ) from acetic acid and two further acyl radicals ( marked in green ), which are derived from propionic acid. The distribution of the ester functions can vary within the polymer chain.
Cellulose acetate propionate (CAP) is a biopolymer based on cellulose . Like cellulose acetate and cellulose propionate, it is an ester of cellulose with aliphatic carboxylic acids . While the esterification of cellulose acetate only takes place through acetic acid , the acetic acid content is around one third, two thirds is bound propionic acid .
Manufacturing
It is produced by esterifying cellulose with a mixture of the anhydrides of acetic acid and propionic acid.
properties
In comparison to cellulose acetate, cellulose acetate propionate is less water-sensitive and better tolerated by plasticizers. At the same time, it is more resistant to aging and weathering than cellulose acetate.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Karlheinz Biederbick: Kunststoffe. 4th edition, Vogel-Verlag, 1977, ISBN 3-8023-0010-6 , p. 170.