The Chow test is a statistical test used to test the coefficients of two linear regressions for equality. The test is named after its inventor, the economist Gregory Chow .
The Chow test is in econometrics used time series of structural changes to test. Another area of application is program evaluation, where two different subgroups (programs), such as two types of schools, are compared with one another. In contrast to the time series analysis, the two subgroups cannot be assigned to successive intervals; instead, the classification is based on a qualitative aspect, such as the type of school.
| Structural break
|
Program evaluation
|
|

|

|
|
If there is a structural break, regressions on the partial intervals and provide better modeling than the regression over the entire interval (dashed)
 ![{\ displaystyle [0; 1,7]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7eda8dec8f44a135c1fdb753dd0f269c02d731ab) ![{\ displaystyle [1,7; 4]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/91fca215a39a5ad0e3a27ed9bb020f92476d8e8f)
|
Comparison of two programs (red, green) in the same data set; separate regressions on the data belonging to a program provide better modeling than the regression over the entire data set (black)
|
Action
Given is a data set with for , the relationship of which is described by a linear function with a normally distributed error ( ) with an expected value of 0 ( ) (multiple regression analysis), i.e. H. One has





-
 for .
for .
It is assumed, however, that the data set can be divided into two groups of sizes and that are better described by two different linear functions.


-
 For
For 
-
 For
For 
Here is and it is tested against the hypothesis . If you denote the sum of the squared residuals of the regression over the entire data set with and over the two subgroups with and , then the test variable defined below follows an F-distribution with degrees of freedom and .










example
The following data set is given, the relationship of which is to be modeled by the linear function :

 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
2.0 |
2.5 |
3.0 |
3.5 |
4.0 |
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.5 |
6.0
|
 |
−0.043 |
0.435 |
0.149 |
0.252 |
0.571 |
0.555 |
0.678 |
3.119 |
2.715 |
3,671 |
3,928 |
3,962
|
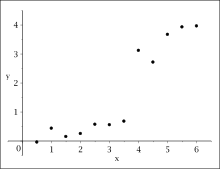
The data plot suggests a structural break at .

A data plot suggests that there is a structural break , therefore the data set is divided into 2 intervals and and over these, in addition to regression over the entire data set, separate regressions are carried out. Then you test whether the two partial regressions generate the same linear function, i.e. against
![{\ displaystyle [0 {,} 5; 3 {,} 5]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bb339edbbc76122ec6a8c9bfcd05b892da3f25c7)
![{\ displaystyle [4 {,} 0; 6 {,} 0]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3f6bf512f84431a3576263290e0cafdbe76a655e)


Regression on the entire data set:
 |

|
 |

|
 |

|
Regression on ![{\ displaystyle [0 {,} 5,3 {,} 5]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7ab416f90870c2504116332118f1890776a14d37)
 |

|
 |

|
 |

|
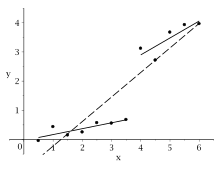
Data plot with regression lines
Regression on ![{\ displaystyle [4 {,} 0.6 {,} 0]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/18af0b593226e3d363819933d712a88c1249c23d)
 |

|
 |

|
 |

|
Calculation of the test size:

Because of (level of significance ) . The null hypothesis can thus be rejected. This means that the two regression lines on the sub-intervals are not identical. There is therefore a structural break and the partial regressions provide better modeling than the regression over the entire data set.




literature
Web links



![{\ displaystyle [0; 1,7]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7eda8dec8f44a135c1fdb753dd0f269c02d731ab)
![{\ displaystyle [1,7; 4]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/91fca215a39a5ad0e3a27ed9bb020f92476d8e8f)



























![{\ displaystyle [0 {,} 5; 3 {,} 5]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bb339edbbc76122ec6a8c9bfcd05b892da3f25c7)
![{\ displaystyle [4 {,} 0; 6 {,} 0]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3f6bf512f84431a3576263290e0cafdbe76a655e)








![{\ displaystyle [0 {,} 5,3 {,} 5]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7ab416f90870c2504116332118f1890776a14d37)







![{\ displaystyle [4 {,} 0.6 {,} 0]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/18af0b593226e3d363819933d712a88c1249c23d)










