Corey Gilman Ganem Oxidation
The Corey-Gilman-Ganem-Oxidation (also Corey-Ganem-Oxidation ), named after its discoverers EJ Corey , NW Gilman and BE Ganem, is a name reaction from organic chemistry and was first published in 1968. The reaction describes the synthesis of esters from aldehydes or allyl alcohols .
Overview reaction
An α, β-unsaturated aldehyde reacts using manganese dioxide , potassium cyanide and methanol to form an α, β-unsaturated methyl ester .
Instead of the aldehyde, allyl alcohol can be used as the starting material. Instead of methanol, another alcohol can be used for the esterification.
Example: Allyl alcohol reacts with the addition of manganese dioxide, potassium cyanide and ethanol to form ethyl acrylate :
Reaction mechanism
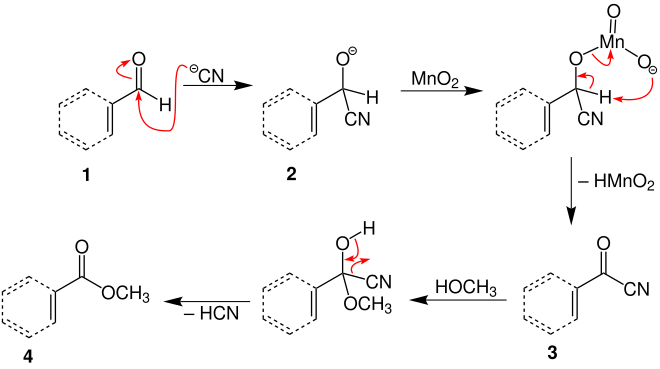
The mechanism is described in the literature and is illustrated using the example of the overview reaction above:
In a nucleophilic attack on the carbon atom of aldehyde 1 caused by the cyanide ion, this reacts to form a reactive ion 2 . Addition of manganese dioxide, resulting electron rearrangement and elimination of hydroxy (oxo) manganese provides intermediate stage 3 . Subsequent addition of the alcohol (here methanol) and subsequent release of hydrogen cyanide creates the ester (here the methyl ester 4 ).
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Elias J. Corey, Norman W. Gilman and BE Ganem: New methods for the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids and esters In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90 (20), 1968, pp. 5616-5617, doi: 10.1021 / ja01022a059 .
- ^ Z. Wang: Comprehensive organic name reactions and reagents Volume 1 . John Wiley, Hoboken (NJ) 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-28662-3 , pp. 722-725 .