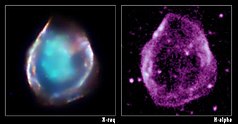
THE L71
The supernova remnant DEM L71 shows a hot inner cloud (aqua) made of glowing iron and silicon , which is surrounded by an external pressure wave . This external pressure wave is also visible at optical wavelengths . Observations show that the central ten-million-degree-Celsius cloud is the remains of a supernova explosion that destroyed a white dwarf star . One can compare the ejected mass of the ejecta with the mass of the sun . It is believed that some white dwarf stars in binary star systems, instead of simply cooling off and quietly disappearing, withdraw enough mass from their companions to become unstable and cause a nuclear detonation . This made it possible to identify this supernova remnant as a Type Ia. The light from the self-destructive explosion of this little star would have reached Earth several thousand years ago.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Chandra :: Photo Album :: DEM L71 :: 12 Mar 03. Retrieved July 4, 2020 .
- ↑ a b APOD: 2003 March 14 - DEM L71: When Small Stars Explode. Retrieved July 4, 2020 .