Digital workplace
A digital workplace is a central digital work platform that provides information, tools and services from anywhere. As an organization-internal web portal , it represents a further development of the intranet . The digital workplace is a collective term for tools that make it possible to work collaboratively and exchange information (see social software ) and this with irreplaceable company applications (e.g. CRM , ERP ) to reconcile.
Office work today and tomorrow
The office is one of the most important parts of most companies and the usual place of work for an employee. With the advent of computers, this concept has become more and more entrenched. Important topics and tasks can be discussed directly with colleagues. For many companies and employees, the physical separation of work and private life is important, which is why work is done in the office.
Please refer:
However, the workplace of the future will move in a different direction. Working independently of time and place is becoming more and more important to employees. The home office principle is already offered in many companies, but so far only eleven percent of all employees have used this option. The reasons are often the company's lack of resources or the mixing of work and private life, which discourages many employees.
Advantages of a digital workplace
The free flow of information in the digital workplace has positive effects on the agility and innovative strength of modern companies. At the same time, it promotes employee engagement and satisfaction by delivering the right information to the right people at the right time. The digital workplace is the "totality of the access infrastructures, applications and device platforms required by information or knowledge workers who need them to carry out their work tasks and to exercise cooperation."
The main advantages of the Digital Workplace are listed as follows:
- Better availability of information and processes
- Support of location and time independent work
- Promotion of company-wide knowledge exchange
- Provision of a central platform instead of numerous isolated solutions
- Simplification of workflows work processes through digitization
- Promotion of commitment and employee satisfaction
Development of a digital workplace
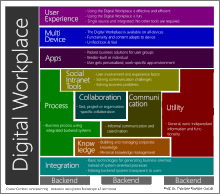
The basic principles of the Digital Workplace are integration and collaboration: data from all software systems used (e.g. ERP, CRM, BI etc.) are brought together on a central platform. This not only provides information and applications, but also promotes cross-location collaboration and the exchange of knowledge.
As a portal, the Digital Workplace is “a solution for integrating information and services in a uniform user interface.” Various services and components are combined in a user interface and usually made available to the user on a web basis. Integrated data can in turn be queried via interfaces and used in other applications. Users can combine existing data and create new applications based on it.
Basically, technically speaking, you can imagine a digital workplace in different layers. The back-end forms the basis. These are the processes and software systems that companies are already using on a daily basis.
The individual basic elements are connected to one another through the process step of data integration. By connecting the data live, the complexity for users can be significantly reduced: the basic applications such as ERP or CRM remain in the background and access is via a uniform and clear front-end.
The individual elements are orchestrated via processes. The software program, machines and data interact with the aim of making information and services available to authorized users in the best possible way. Numerous processes can run automatically here.
The graphical processing of the integrated data and the implemented processes takes place in applications that are directly embedded in the surface of the web-based digital workplace. Access to the data is personalized and related to the work processes. The applications at the Digital Workplace can be adapted to the circumstances of the respective company and thus optimally map the individual work processes.
Social collaboration aspects ensure that company-wide collaboration is encouraged. Employees can actively exchange knowledge and communicate on projects, etc. This aspect becomes particularly important if you want to work together across different locations or departments.
After all, the accessibility of the digital workplace plays an immense role. In order to provide a really modern work environment, it must be location-independent and accessible via various end devices. This is the only way to sensibly support scenarios such as home office and flexible work in terms of time and space. The provision of information and processes must always be secure and encrypted.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Kruse, Paul, Geißler, Peter (eds.): The networked company How the digital workplace is redesigning our collaboration . 1st edition Norderstedt 2015, ISBN 978-3-7392-9620-3 .
- ↑ Sabine Menkens: When it comes to home offices, Germany is still a developing country . In: Welt Online . May 25, 2016 ( welt.de [accessed on August 11, 2016]).
- ^ Frank Schönefeld: Social Intranet - The new role of the intranet for the digital workplace . In: Frank Wolf (Ed.): Social Intranet - Promote communication - Share knowledge - Work together efficiently . Carl Hanser Verlag, 2011, ISBN 3-446-42791-0 , p. 14-40 .
- ↑ Jane McConnell: Trends for Intranet and Digital Workplace . In: Frank Wolf (Ed.): Social Intranet - Promote communication - Share knowledge - Work together efficiently . Carl Hanser Verlag, 2011, ISBN 3-446-42791-0 .
- ↑ a b Michael Koch, Alexander Richter: Enterprise 2.0 - Planning, introduction and successful use of social software in companies . Oldenburg Verlag, Munich 2009.