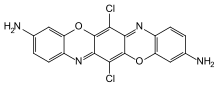
Dioxazine colorants
Dioxazine colorants , i.e. dioxazine dyes and dioxazine pigments, are polycyclic chromophores . They contain two 1,4-oxazine units and are derived from the basic structure of triphendioxazine ( IUPAC : [1,4] benzoxazino [2,3- b ] phenoxazine). The unsubstituted triphendioxazine is colored orange, but has no meaning as a colorant .
history
Colorants based on the triphendioxazine chromophore have been known since 1928. At that time, the sulfonated derivatives , which were known under the common name Sirius light blue , were particularly important . CI Pigment Violet 23, known under the common name Carbazole Violet, was only discovered in 1952, but was quickly used commercially. This pigment is still the most important representative of this group of colorants today. Of the other derivatives, only CI Pigment Violet 37 is important as a niche product today.
effect
Electron donors at positions 2, 3, 6, 9, 10 and 13 cause a bathochromic shift in the absorption band. Such derivatives are strongly colored , lightfast and brilliant, violet to blue chromophores.
presentation
Starting from chloranil (2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone) and two parts of 1,4-diaminobenzene, 2,5-bis [(4-aminophenyl) amino] -3,6-dichloro- Represent 1,4-benzoquinone, which can be oxidatively cyclized in oleum . The dioxazine colorants on the market today that are based on this basic structure are all symmetrical. However, unsymmetrical dioxazine colorants are also described in the literature.
use
Dioxazines are strong, universally applicable colorants. In deep tones, they have excellent light, weather and varnish fastness and are relatively thermostable (~ 150 ° C). As with all colorants, the fastness properties are less good in lighter shades. They are used in paints (paint, industrial, automotive and powder coatings ) and in emulsion paints . These pigments are also used in paper printing.
Pigments
Important commercial products are the violet pigments CI Pigment Violet 23 and, to a lesser extent, CI Pigment Violet 37.
CI Pigment Violet 23
CI Pigment Violet 23 (also called Carbazole Violet) is the most strongly colored commercial organic pigment. It is used for coloring plastics and lacquers, for printing inks and in other special areas, such as artist paints or in purple candles. It is often used in paints to shade copper phthalocyanine . In this way, a slight red cast is achieved for the pure blue of the copper phthalocyanine.
CI Pigment Violet 23 has good light and weather fastness. Like most organic pigments, it is practically insoluble in all media and therefore non-toxic. CI Pigment Violet 23 has an S-shaped structure:
An incorrect structural formula for the linear isomer is still often found in the literature. The correct structure was determined in 1987 by an X-ray structure analysis. The industrial synthesis of CI Pigment Violet 23 is shown in the drawing. The linear isomer can be synthesized in a different way in the laboratory, but because of its more complex and expensive synthesis, it was never produced industrially.
CI Pigment Violet 37
CI Pigment Violet 37 has a slightly more reddish cast than CI Pigment Violet 23. It is produced in smaller quantities and mainly used in metal decorative printing.
CI Pigment Blue 80
In 2001 a combination of dioxazine violet and benzimidazolone was presented as a benzimidazolone- modified dioxazine pigment and registered as CI Pigment Blue 80. Formally, the carbazole residues have been replaced by benzimidazolone residues, which combines the fastness properties (especially light and weather resistance) of benzimidazolone pigments with the color strength of dioxazines. The molecule has the linear shape shown as shown by NMR spectroscopy and crystal structure analysis from X-ray powder diagrams. The pigment has a reddish blue hue. However, the commercial products could not establish themselves on the market.
Dyes
In contrast to the pigments , which by definition are insoluble in their application medium , dyes are soluble. Water-soluble dioxazine dyes, as they are commonly used in textile dyeing, are achieved by introducing hydrophilic groups ( sulfonation ). Many direct dyes are derived from this structure . However, suitable reactive anchors (here cyanuric chloride ) can also be coupled to the amino groups , which means that reactive dyes for dyeing cotton can be produced. With this group of dyes, cotton is dyed brilliant blue with very good wet fastness properties.
literature
- W. Herbst, K. Hunger: Industrial Organic Pigments . 3rd Edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2004.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b P. Kempter, G. Wilker: Blue remains blue . In: Farbe und Lack 11/2001; Page 29.
- ↑ German patent DE19859904A1 Asymmetrical dioxazine compounds and method for dyeing or printing a fiber material using the same .
- ↑ a b M.U. Schmidt: Imidazolone-annellated triphendioxazine pigments . In: High Performance Pigments , edited by EB Faulkner and Russel J. Schwartz, 2nd edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2009, pages 341-354.