Honest Sachs reaction
The Ehrlich-Sachs reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry, which was first introduced in 1899 by the German researcher Paul Ehrlich (1854–1915) and Franz Sachs and was later named after the discoverers.
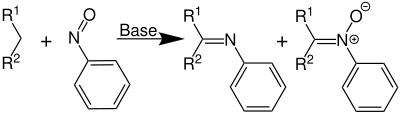
Overview reaction
This reaction is the condensation between a compound with an active methylene group and an aromatic nitroso compound . The reaction can be triggered by bases , acids or heating. In this reaction two competing products are formed, an azomethine ( Schiff base ) and an oxidized nitrone derivative :
The use of a weak base - such as sodium carbonate - is sufficient to start the reaction.
Reaction mechanism
The mechanism of this reaction has not yet been finally clarified. It is assumed that the nitrogen of the nitrosobenzene forms a connection with the central carbon deprotonated by the base . The resulting compound is deprotonated again by the base, as a result of which the double bond is formed. It is assumed that the reaction conditions, the acidity of the methylene group and the structure of the compound with the methylene group can influence the reaction result. If enolates are formed from the 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds or aryl - alkyl - ketones as a result of the base, the azomethine derivatives are mainly formed in the reaction.
application
This reaction is commonly used in the manufacture of azomethine derivatives in the dye and pharmaceutical industries.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ehrlich-Sachs Reaction . In: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents . Wiley, 2010, ISBN 978-0-470-63885-9 , pp. 964-966 , doi : 10.1002 / 9780470638859.conrr208 .