Gattermann reaction
The Gattermann reaction , or Gattermann method, is a name reaction in organic chemistry, which was first introduced in 1890 by the German chemist Ludwig Gattermann (1860–1920) and named after him. It describes the preparation of aromatic halides or aromatic nitriles by decomposing corresponding diazonium salts in the presence of copper powder . The copper powder is freshly obtained from an aqueous copper (II) sulfate solution.
This reaction is not suitable for the production of fluoroaromatics.
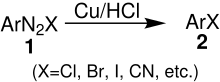
Overview reaction
In this reaction, an unstable diazonium salt 1 is decomposed to form an aryl halide 2 . It is believed that this reaction involves a radical process in which an electron transfer takes place on the surface of the metallic copper.
Reaction mechanism
Two different reaction mechanisms are discussed. In both variants, the copper is available again for new reactions at the end of the reaction chain.
Reductive elimination of copper
When diazonium salt 1 reacts with copper, the copper atom inserts between the phenyl radical and the diazo group. Intermediate 3 is formed from intermediate 2 with chloride with elimination of nitrogen . The copper 4 is eliminated reductively from 3 with the formation of chlorobenzene 5 .
Radical reaction mechanism
When 6 is heated , a homolytic bond breakage takes place between the phenyl radical and the copper atom, with the formation of two radicals , see 7 . Subsequently, copper is split off through radical rearrangements and chlorobenzene 5 is formed.
modification
In a modified Gattermann reaction, the aryl halides are prepared from aryldiazonium salts, which are stabilized by the anion of the o -benzenesulfonimide and can be dried. The reaction of these aryldiazonium o -benzenesulfonimides with quaternary ammonium halides in the presence of copper gives aryl halides.
Example reaction:
In this example , tetrabutylammonium bromide 2 is added to a suspension of benzene diazonium o -benzene disulfonimide 1 in acetonitrile . In the presence of copper, bromobenzene 3 is formed as a colorless oil with a yield of 86%. The copper can be removed and reused by simple filtration.
Related reactions
This reaction is related to the Sandmeyer reaction , the Balz-Schiemann reaction and the Bart reaction . It is particularly similar to the Sandmeyer reaction.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Zerong Wang: Gattermann Reaction . In: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents . John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA 2010, ISBN 978-0-470-63885-9 , doi : 10.1002 / 9780470638859.conrr265 .
- ↑ Margherita Barbero, Marco Crisma, Iacopo Degani, Rita Fochi, Paolo Perracino: New Dry Arenediazonium Salts, Stabilized to at Exceptionally high degree by the anion of o-Benzenedisulfonimide . In: Synthesis . tape 1998 , no. 08 , p. 1171 , doi : 10.1055 / s-1998-2132 .
- ^ Carlo Galli: Radical reactions of arenediazonium ions: An easy entry into the chemistry of the aryl radical . In: Chemical Reviews . tape 88 , no. 5 , 1988, pp. 765-792 , doi : 10.1021 / cr00087a004 .