Stretched exponential function
As stretched exponential called mathematical function is a generalization of the exponential function with an additional parameter in the exponent :
or, with :
- .
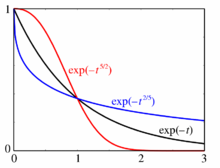
In most applications , what goes hand in hand with the eponymous stretching: the function drops more slowly than the usual exponential function . For we get the compressed exponential function , for the Gaussian function . Application is, among other things, the Weibull distribution .
The extended exponential function was introduced by Rudolf Kohlrausch in 1854 to describe the relaxation of the electrical polarization of a capacitor with a glass dielectric .
The stretched exponential function is also known as the Kohlrausch function or Kohlrausch-Williams-Watts function , after Graham Williams and David C. Watts , who rediscovered it in 1970.
Individual evidence
- ↑ R. Kohlrausch: Theory of the electrical residue in the Leidner bottle. In: Annalen der Physik und Chemie Vol. 91, 1854, pp. 56–82, 179–214; online (pp. 56-82) online (pp. 179-214) .
- ^ G. Williams, D. C. Watts: Non-Symmetrical Dielectric Relaxation Behavior Arising from a Simple Empirical Decay Function. In: Transactions of the Faraday Society Vol. 66, 1970, pp. 80-85; doi : 10.1039 / TF9706600080