Ghosez cyclization
The Ghosez cyclization is a name reaction in organic chemistry, which was first introduced in 1988 by the Belgian chemist Léon Ghosez (* 1934) and named after him.
Overview reaction
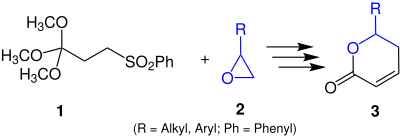
In this reaction, phenylsulfonyl-orthobutyric acid trimethyl ester 1 is cyclized to a δ- lactone 3 by means of an epoxide 2 .
Reaction mechanism
First, the orthoester 1 is deprotonated with butyllithium (n-BuLi) , so that a negative charge arises on the carbon atom next to the phenylsulfonyl group 2 and this can attack the epoxide nucleophilically. Subsequently, the now negatively charged oxygen atom of the former epoxide can nucleophilically attack the central carbon of the orthoester 3, whereby a methyl alcoholate can split off and leave. In the following step 4, methanol is split off twice by protonation . This creates a precursor 5 of the desired lactone. This precursor can be deprotonated by adding diazabicycloundecene (DBU) and the phenylsulfonyl group is split off 6 , whereby the end product 7 is formed.
application
The Ghosez cyclization is used for the CC linkage in the synthesis of complex molecules, for example in the total synthesis of Swinholid A, a marine natural product with fungicidal and antineoplastic effects.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Zerong Wang: Ghosez Cyclization: (Ghosez Lactonization) . In: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents . John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA 2010, ISBN 978-0-470-63885-9 , doi : 10.1002 / 9780470638859.conrr268 .
- ↑ KC Nicolaou, Dionisios Vourloumis, Nicolas Winssinger, Phil S. Baran: The state of total synthesis in the early 21st century . In: Angewandte Chemie . tape 112 , no. 1 , January 3, 2000, p. 46 , doi : 10.1002 / (SICI) 1521-3757 (20000103) 112: 1% 3C46 :: AID-ANGE46% 3E3.0.CO; 2-P .