Hadriacus Mons
| Volcano on mars | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hadriacus Mons / Hadriaca Patera | ||
|
||
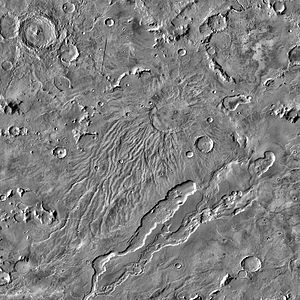
| Hadriacus Mons with the Valles in the lower part of the picture. | ||
|
|
||
| position | 31 ° 17 ′ S , 91 ° 52 ′ E | |
| expansion | 450 km | |
| height | 1100 m | |
The Hadriacus Mons (also Hadriaca Patera) is an extinct volcano on Mars . He is older than the neighboring Tyrrhenus Mons . It stands on the edge of a low plain in which the lava flows could extend over several hundred kilometers. The volcanoes on the red planet have not been active for millions of years. Hadriacus Mons has a diameter of 450 km (330 km * 550 km) and is 1.1 km high. The caldera has a diameter of 90 km and is 700 m deep.
description
The caldera of the volcano, is 30 ° 12 ' S , 92 ° 47' O . On the southern slope of the river valley 794 km long Dao Vallis began ( 37 ° 37 ' S , 88 ° 53' O ) and extends to the east due to the Mars crater Hellas Planitia . The Dao Vallis is extended by the 360 km long Niger Vallis ( 34 ° 58 ′ S , 92 ° 34 ′ E ), beginning on the southeastern slope of the volcano. Further south the 527 km long Stromtal Harmakhis Vallis (runs 40 ° 59 ' S , 90 ° 4' O ), which also ends at the east due to the Mars crater.
Web links
- raumfahrer.net: Mars Express: The Hadriaca Patera volcano, May 21, 2012 , images from the CTX camera on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) with a resolution of eight meters per pixel show the process of fracture formation, collapse and erosion of the river valleys from Hadriacus Mons.