Horatio Frederick Phillips
Horatio Frederick Phillips (born February 2, 1845 in Streatham , † 1924 in London (other sources: July 15, 1926 in Hampshire)) was an English engineer and aviation pioneer. He became famous in 1907 for his first manned powered flight in England.
Life and works
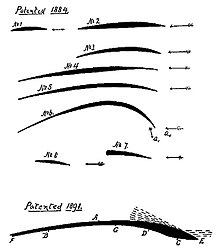
The son of a gunsmith, Horatio Frederick Phillips was born in a suburb of London in 1845. He reportedly became a member of the Royal Aeronautical Society at a young age, researching the aerodynamic impact of wing profiles . At the age of 27, Phillips built a wind tunnel in which he developed and examined a variety of wing shapes and profiles. In the wind tunnel, Phillips used a gas stream made up of steam instead of pure air and, during the test series, revived George Cayley's idea with curved surface profiles that significantly improved the lift on aircraft wings. In 1884 he was able to register his first profile patent and more were to follow.
Proving Ground
With an unusual arrangement, Phillips tested his flying machines with new profiles in the open-air area in front of the building with the wind tunnel by tying his test flying machines to a pole, which followed on ropes along a paved circular path with a diameter of around 61 meters. In this way he was able to carry out the first flight tests and measurements in original size without loss. Only tests with small models or individual profiles were possible in the wind tunnel.
HFP flying machines
In 1893 Phillips was able to convert a remarkable device with curved wings from theory to practice. The simple flying machine, known as the Phillips Flying Machine , consisted of a slim, cigar-shaped fuselage with a small motor with a propeller and a wing frame with 50 narrow wing profiles.
In 1904 he developed a multi-decker (Multiplane). The wings consisted of 20 individual, narrow aerodynamically shaped wings arranged one above the other. The aircraft, which weighs around 272 kilograms (600 lbs including pilot and motor), was able to fly at a flow speed of 50 ft per second (15.24 m / s), which corresponds to a flight speed of 54 km / h. However, the machine only performed a short “jump in the air”.
Horatio Frederick Phillips built another aircraft in 1907, which consisted of 200 multilevel wings with a 20 hp engine and carried out the first manned powered flight in Great Britain on April 6, 1907. It reached an altitude of 500 feet (150 m). The airspeed was 30 mph (48 km / h). The Royal Aeronautical Society published the reports on the work of Phillips in 1907.
Horatio Frederick Phillips died in 1924 at the age of 79. His profile research is a milestone in the progress of later aviation history.
literature
- Aeronautical Journal, Volumes 11-12, 1907
- Horatio Phillips & Multiplanes
- Horatio F. Phillips Flightglobal Archive 1907
Individual evidence
- ↑ Biographical Dictionary of the History of Technology , Taylor & Francis, 2003 - History - 864 pages ISBN 978-0-203-02829-2
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Phillips, Horatio Frederick |
| ALTERNATIVE NAMES | Phillips, Frederick |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | English engineer and aviation pioneer |
| DATE OF BIRTH | February 2, 1845 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Streatham |
| DATE OF DEATH | around 1924 |
| Place of death | London |