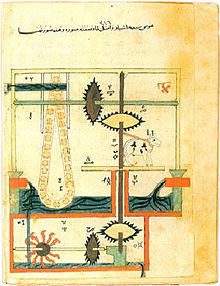
Chain pump
A chain pump is a mechanical conveying mechanism ( pumping mechanism ) for liquids, which consists of a revolving chain with discs, shovels or tufts that lift the liquid (water, liquid manure, etc.) up in a pipe or with buckets, boxes, beakers or other containers that hold water at the bottom and pour it out at the top.
In the case of chain pumps with pulleys, the chain runs down over an upper wheel that is driven, is deflected there by another wheel and then runs up again in a pipe. The discs take the water in the pipe and push it upwards. Instead of discs, cushions or padded balls (tufts) can also be used.
Other names are paternoster work (because the chain runs endlessly like a paternoster lift ), rosary mill, chain art, disk art.
Chain pumps are already known from the Chinese Empire (earliest Chinese mention in the Han dynasty by the philosopher Wang Chong around the year 80 ). Ma Jun (220–265) is named as the designer of a chain pump, if not the first inventor. In the Arab world, Al-Jazari has constructed chain pumps , among others . In Persia, the " Persian pump " is known, a kind of bucket wheel that is operated with a chain.
Because of the high friction of the moving parts and the water losses, chain pumps have a low level of efficiency .