Block frieze
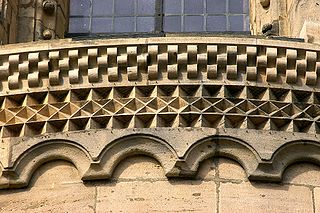
A block frieze or cube frieze or chessboard frieze (in a rounded shape also known as a roller frieze or roller frieze ) is an architectural decorative element made of small stones that alternate in height.
material
Although it would have been possible to work on wooden beams in a similar way and with much less effort, block friezes were exclusively and laboriously carved out of larger stones (mostly tuff or sandstone ).
species
Multi-row or flat block friezes often appear on eaves cornices in Romanesque churches. More rarely, pillars or arches are decorated with block patterns.
Also dentil motives are often referred to as blocks Friese; they can be found on inside and outside walls. Sometimes the fighters of half-column templates are included in the simply lined up block frieze (tooth cut).
history
Antiquity
Although block friezes are very likely to be associated with brick construction or with checkerboard patterns, they do not occur in the decor of antiquity or have not been preserved.
middle Ages
Block friezes experience their heyday in Romanesque architecture of the Middle Ages. They disappear again in the Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque periods, only to reappear in the historicizing art of the 19th century.
symbolism
A symbolic content of block friezes, which in a broader sense must be included in the grid shapes, cannot be proven. However, since they appear almost exclusively outside and also at transition points such as eaves cornices, window reveals, etc., an originally disastrous ( apotropaic ) meaning cannot be completely ruled out.
photos
Marmoutier (Alsace) - Block frieze in the window reveal
St. Peter (Sinzig) - 4-fold lined block frieze under the eaves
Ste-Foy de Sélestat - single row block frieze (tooth cut)


