Cerebellar bridge angle
The cerebellar bridge angle ( Angulus pontocerebellaris ) is a niche-like depression on each side of the posterior brain base, which is delimited by the cerebellar tonsils and the caudal bridge edge or the elongated marrow of the brain stem.
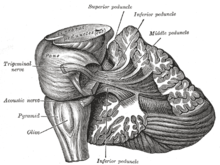
In the cerebellopontine angle , the central parts of several cranial nerves and central blood vessels run in a narrow space at the base of the brain and in the posterior fossa cranii posterior near the petrous pyramid . In particular, this area of VII through them. ( Facial nerve ) and VIII. Cranial nerve ( vestibulocochlear nerve ), which converge in the cerebellum bridge angle, as well as the front and rear lower cerebellar artery ( anterior inferior cerebellar artery or A. inf. Posterior cerebelli ) , as well as venous blood conductors ( sinus petrosi ).
Pathological processes in the cerebellopontine angle often lead to complex symptoms , which can include functional failure of the cranial nerves (mostly VII. And VIII.) And the cerebellum, as well as signs of increased intracranial pressure . Common causes for this are masses, usually an acoustic neuroma , more rarely other tumors , local inflammatory processes or altered blood vessels .
Web links
- Photographic image of the cerebellopontine angle in situ
- Patient information on foci of disease in the cerebellopontine angle and posterior fossa with images
Individual evidence
- ↑ cerebellopontine angle. Roche Lexicon Medicine, 5th edition, Urban & Fischer 2003
- ^ Cerebellopontine angle and posterior fossa . In: Neurosurgical University Clinic Freiburg . January 26, 2007. Archived from the original on July 20, 2006. Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved January 27, 2007.
- ↑ B. Holst et al .: Differential diagnosis of masses in the cerebellopontine angle. Radiologist. 2004 Nov; 44 (11), pp. 1113–1136, PMID 15526182 ( German summary ( memento of the original from October 2, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. )
- ↑ a b J. Maurer: Vascular causes of the "cerebellopontine angle syndrome"? ENT. 2000 Feb; 48 (2), pp. 142-146, PMID 10663063 . doi : 10.1007 / s001060050022 .
- ↑ Symptoms of the cerebellopontine angle. In: Roche Lexicon Medicine . 5th ed. Urban & Fischer, 2003