LEOPARD syndrome
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| Q87.8 | Other specified congenital malformation syndromes, not elsewhere classified |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The LEOPARD syndrome refers to congenital malformations of the heart and skin and is therefore also called " cardio cutaneous syndrome ". It is a variant of Noonan's syndrome in which pulmonary stenosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are the salient cardiac phenotype. Half of the LEOPARD and Noonan syndromes are inherited sporadically and half are autosomal dominant. The responsible gene is located on chromosome 12q22 and encodes the synthesis of protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 11 (PTPN11) .
LEOPARD as an acronym stands for:
- Lentiginosis
- ECG -Changes: bundle branch block
- Ocular : hypertelorism
- Pulmonary stenosis and subvalvular aortic stenosis
- Anomalies of the genital organs: hypospadias , cryptorchidism , gonadal suppression
- Retarded growth: skeletal abnormalities such as funnel chest , scapula alata , hyperextensibility of the joints
- Deafness (English d eafness ) sensorineural
The lentigines (as in the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome ) indicate a systemic disease . Hundreds of them appear in childhood on the entire surface of the body , and with increasing age they pale in the face, but not in the oral cavity.
Treatment of the syndrome is symptomatic .
Clinical aspect
Two year old child with multiple lentigines on the trunk and proven PTPN11 gene mutation
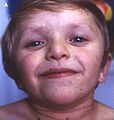
5 year old child with LEOPARD syndrome, cafè-au-lait spots and signs of dysmorphism : hypertelorism , ptosis , blue sclera , low onset of dysmorphic ears
literature
- A. Sarkozy, MC Digilio, B. Dallapiccola: LEOPARD syndrome. In: Orphanet J Rare Dis. 3, 1, 13th 2008. doi: 10.1186 / 1750-1172-3-13 . PMID 18505544 , full text online (English)
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ M. Dietel, N. Suttorp, M. Zeitz, DC Kasper, E. Braunwald, AS Fauci, SL Hauser, DL Longo, JL Jameson (eds.): Harrison's internal medicine. German edition in cooperation with the Charité. 16th edition. McGraw Hill, ABW-Wissenschaftsverlag, Berlin 2005, ISBN 3-936072-29-9 .
- ^ AJ Marian, R. Brugada, R. Roberts: Cardiovascular Diseases Due to Genetic Abnormalities. In: V. Fuster, W. Alexander, RA O'Rourke (ed.): Hurst's The Heart. 11th edition. McGraw-Hill, New York 2004, ISBN 0-07-142264-1 , p. 1757.