Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
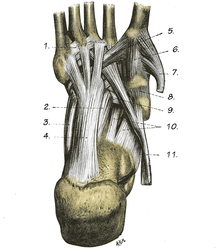
The ligamentum calcaneonaviculare plantare (Syn. Ligamentum calcaneocentrale plantare , " acetabular ligament ", "flat foot ligament ", English: spring ligament ) is located on the plantar side (sole of the foot ) of the foot and connects the heel bone ( calcaneus ) with the navicular bone (scaphoid bone, Syn. Os tarsi centrale ).
It is conical in shape and runs between the sustentaculum tali and the plantar side of the navicular bone . This area of the foot skeleton bears the head of the talus ( talus ). Its dorsal surface forms part of this joint. The band therefore has a cartilage coating. Since this joint is reminiscent of a pan, the band is also called the “pan band”. The tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle runs over its plantar side .
The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament plays a key role in stabilizing the arch of the foot. If it gives way, the medial part of the longitudinal arch flattens out and flatfoot develops (hence the synonym “flatfoot ligament”).