Magnetorheological elastomers
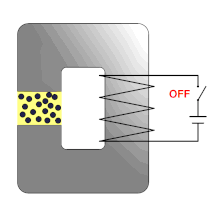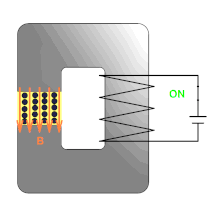
Magnetorheological elastomers ( MRE ) usually consist of an elastomer matrix and the magnetically active particles dispersed in it . With these elastomers, the viscoelastic or dynamic mechanical properties can be changed quickly and reversibly by applying an external magnetic field .
There are two different physical interpretations of the magnetorheological ( rheology : deformation and flow properties of matter) effect. One approach describes the dipole-dipole interaction (similar to magnetorheological fluids ), the other assumes a distortion of the magnetic field in the immediate vicinity of each particle and the resulting magnetic inhomogeneity forces.
Areas of application
The main interest in these materials lies in their use in mechatronic systems , as they can form a robust and simple interface between the control electronics and the mechanical components. While conventional passive elastomer materials are used in components for suspension, vibration isolation and sealing, controllable elastomer components can fulfill much more far-reaching tasks. A main focus of the application of MR elastomers can for example be the variably adjustable suspension of vibrating parts. They can therefore be used as semi-active bearing elements, bushings or as suspensions with variable rigidity. Another area of application for this class of materials is in the field of shielding against electromagnetic radiation, which is particularly important in the field of communication and radar technology .
literature
- Thomas Alshuth, M. Ramspeck, Robert H. Schuster, Bernd Halbedel, Florian Zschunke: Magnetorheological Elastomers. Influence of particle orientation on switchability. In: rubber, rubber, plastics. International trade journal for polymer materials. Vol. 60 (2007), issue 9, pp. 448-455, ISSN 0022-9520 .