Metal-to-metal bond
A metal-metal bond in the narrower sense is a directed chemical bond between individual metal atoms . In contrast, the metallic bond is an undirected bond between many metal atoms.
The metal-metal bond in the narrow sense comes about through one or more shared electron pairs and is therefore an electron pair bond . Depending on the number of binding electron pairs (one, two, three, four or five), it is a single , double , triple , quadruple or fivefold bond .
Compounds with a metal-to-metal bond, especially if they have more than two connected metal atoms, are also known as metal clusters .
Examples
- Single bond : [Mn 2 (CO) 10 ], [Re 2 (CO) 10 ], [Mo 2 Cl 9 ] 3− . There is also a metal-to-metal single bond in diiron nonacarbonyl [Fe 2 (CO) 9 ], although there are arguments against this bond.
- Double bond : [Re 3 Cl 9 ] in rhenium (III) chloride
- Triple bond : [W 2 Cl 9 ] 3−
- Quadruple bond : [Re 2 Cl 8 ] 2− , octamethyldimetallate anions: [Cr 2 Me 8 ] 4− , [Mo 2 Me 8 ] 4− , [W 2 Me 8 ] 4−
- Five-fold binding : e.g. B. between chromium or uranium atoms
- Sixfold bond: discussed for the bond in the diatomic molecules dimolybdenum Mo 2 and di-tungsten W 2 .
Monovalent compounds of mercury and related structures
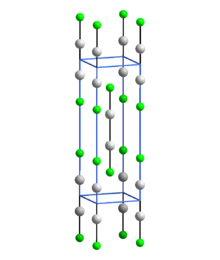
All mercury (I) compounds, e.g. B. the halides mercury (I) fluoride Hg 2 F 2 , mercury (I) chloride Hg 2 Cl 2 , mercury (I) bromide Hg 2 Br 2 and mercury (I) iodide Hg 2 I 2 , and that monovalent mercury (I) oxide Hg 2 O and the mercury (I) nitrate Hg 2 (NO 3 ) 2 , containing an array of two mutually bound mercury atoms, d. H. a Hg – Hg bond . With the ligands bound to it (L e.g. F, Cl, Br, I) a linear, i.e. H. L-Hg-Hg-L structure lying on a straight line.
There are also known mercury polycations which consist of chains of mercury atoms bonded to one another, which carry a total of two positive charges, such as Hg 3 2+ .
In the case of zinc and cadmium, the monovalent oxidation state is less stable and therefore rarer. At elevated temperatures, a mixture of zinc and ZnCl 2 has increased volatility, which is explained by the presence of Zn 2 Cl 2 . Monovalent cadmium is contained in the chloroaluminate Cd 2 [AlCl 4 ] 2 .
Metal fumes
Lithium vapor contains around 1% Li 2 molecules, sodium vapor around 16% Na 2 molecules.
Individual evidence
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1785.
- ↑ Jee Hwan Jang, Jung Goo Lee, Hosull Lee, Yaoming Xie, Henry F. Schaefer III: Molecular Structures and Vibrational Frequencies of Iron Carbonyls: Fe (CO) 5 , Fe 2 (CO) 9 , and Fe 3 (CO) 12 . In: Journal of Physical Chemistry A . tape 102 , no. 27 , 1998, pp. 5298-5304 , doi : 10.1021 / jp981356o .
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , pp. 1626-1627.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1495.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1260.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1273.
