Monobactams
| Monobactams with the β-lactam ring marked blue |
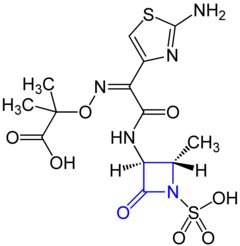 Aztreonam |
 Tigemonam |
Monobactams ( e.g. aztreonam and tigemonam) are drugs that are used as antibiotics .
Manufacturing and structure
Monobactams are semi-synthetic antibiotics. They are produced by gram-negative bacteria and then synthetically modified. Like many other β- lactam antibiotics, they contain a monocyclic β-lactam ring but no further fused-on ring.
application
Monobactams are β-lactamase -stable, but are cleaved by Extended Spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL). They are not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and must therefore be administered parenterally . Their spectrum of activity includes only gram-negative pathogens. They show no effect on anaerobic and gram-positive germs. Their therapeutic application is mostly on individuals with penicillin - and cephalosporin - allergy limited.
Individual evidence
- ^ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals , 14th Edition (Merck & Co., Inc.), Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006; P. 156, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .