Multihoming
Multihoming is a technique in which a device has several network addresses.
Internet connections
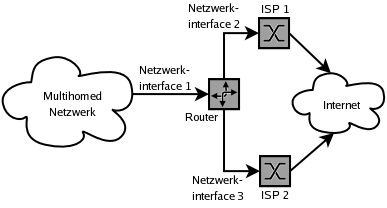
One application of multihoming is to make Internet connections redundant. For this, the connection is made to the Internet via at least two ISP ( Internet service provider , ISP). If the connection to one of the Internet providers fails, the router automatically switches all routes that previously ran through it to the other providers.
Multihoming is usually implemented via BGP routers (e.g. Cisco router or Linux server with Quagga ). Due to the different AS path lengths, it decides by default which ISP connection is preferred for a particular connection. By using various tuning parameters (MED, Precedence) of the BGP protocol, data can be routed via an Internet connection, depending on their target network.
In this case, multihoming requires that PI addresses ( provider independent ) are used in the network or that networks assigned to the customer (AS) from the PA address range of one provider are also accepted by the other provider as the sender address. If this is the case, other traffic shaping mechanisms can also be used to e.g. B. to run all incoming data packets through one ISP and the outgoing through a second. Another (not widespread) variant is to split the individual Internet services such as web, FTP, database, etc. over the two Internet lines.
server
In practice, servers are always connected to several network cards . A server has at least two and typically four network interfaces.
In a setting with four interfaces, two interfaces are used to process client requests redundantly. The third interface is used to enable remote maintenance of the server via a LAN or VLAN that is separate from the public network . The fourth interface is a separate connection to handle bandwidth-intensive traffic with high priority, such as the backup in particular . The connection to the backup storage can either be designed as NAS , SAN or SAS .
If only two network interfaces are available, one interface is reserved for client inquiries, while the second interface is used for remote maintenance and backup.
Servers are sometimes given additional network addresses (and network interfaces) in order to separate public data traffic from internal data traffic (via a VLAN). This makes it possible to increase the security of the internal network, for example as protection against overload and hacker attacks .
Multihoming with a single network interface
A single network interface can also be used for multihoming by assigning multiple network addresses to it.
Examples:
- Simultaneous support of IPv4 and IPv6 or other network protocols over the same interface
- Routing between multiple networks using a single interface (" Router-On-A-Stick ") using virtual LANs ( VLAN - Trunk ).
- Mapping of network addresses of the host system to different virtual machines
See also
- Bundling (also: bonding or teaming ; several interfaces with the same network address)
credentials
- ↑ a b c Michael T. Nygard: Release It! Design and Deploy Production-Ready Software. O'Reilly, 2007, ISBN 978-0-9787392-1-8 , 11.1 Multihomed Servers (English, 326 pages).
- ↑ Bradley Mitchell: What Is Multihoming? In: lifewire. September 7, 2016, accessed March 3, 2017 .