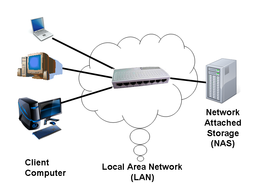
Network attached storage
Network Attached Storage ( NAS , English for network- attached storage ) refers to easy-to-manage file servers . A NAS is generally used to provide independent storage capacity in a computer network without great effort .
Clarification of terms, definition
Today's personal computers (PCs) usually have a hard drive that is built directly into the computer's housing and store their directories and files there. One speaks of local storage, which is usually only available to users who work directly on the computer.
If a hard drive with the files stored on it is to be available across the network, i.e. to be accessible from all computers in the network, the storage system must first be connected directly to the network and also master transmission protocols that make the files available on this storage space in the connected computer network . This functionality is provided by file-based network protocols such as SMB / CIFS and NFS or block-based network protocols such as iSCSI and FCoE . One then speaks of "storage that is connected to a network", i.e. Network Attached Storage or NAS for short. NAS systems are connected directly to the network and work autonomously, i. H. without the need for a dedicated PC or server. The file systems of the NAS, i.e. all files and directories created there, appear on the target system like an integrated share or a local file system.
NAS systems in the narrower sense are server services that make ready-to-use file systems available to clients connected via a network service, depending on the operating system. This separates the service from Direct Attached Storage (DAS) and Storage Area Network (SAN) . NAS systems in the broader sense, as offered in practice, provide central storage space on disk arrays with both file-based and block-based access via the general network. The general network is usually the Ethernet-based LAN , and increasingly also WLAN .
Advantages of a dedicated NAS system
- power consumption
- NAS systems have a significantly lower power consumption compared to conventional PC systems.
- File access
- NAS can handle large amounts of data and allow multiple users to access data at the same time. By using high-performance hard disks and caches , even large amounts of data can be made quickly accessible to the user. Professional NAS solutions are suitable for consolidating file services in companies. High-performance, redundant and fail-safe NAS solutions represent an alternative to traditional Windows / Linux / Unix file servers. To simplify the data backup of large NAS environments, most devices in this class support the Network Data Management Protocol . Alternatively, a NAS can also be used as a backup solution for existing computers .
- Data security / transmission speed
- NAS systems can be equipped with several hard disks that can be combined into a logical volume in a RAID . With 2 or more hard disks, this enables higher capacity, security or speed. There are differences, especially with regard to the type of hard drive used. In contrast to DAS hard disks, so-called NAS hard disks are designed or constructed for continuous operation. SSD drives have also been used in high-quality NAS since around 2010, which further improves transfer rates and failure rates.
Functions
A NAS generally provides file server functions. This means user access to files via a local network . Especially when used in a professional environment, the systems must be able to take into account access rights ( ACL ) for users registered in the network ( data protection ). A common appearance is personal data that is only accessible to one user or group data that is accessible to groups of several users.
A NAS thus provides far more functions than just assigning storage to a computer over the network. Therefore, in contrast to direct attached storage , a NAS is always either an independent computer ( host ) or a virtual computer (virtual storage appliance, VSA for short) with its own operating system . Many systems have RAID functions to prevent data loss due to defects and / or to increase transmission speeds. File-based services such as NFS or SMB / CIFS represent the core function. Some more extensive NAS implementations such as FreeNAS , OpenMediaVault or Openfiler also master block-based data access, as is common with DAS or SAN , and offer an iSCSI implementation for this . This variety of functions is often summarized in the term filer .
For use in small home and so-called SoHo networks, Network Direct Attached Storage has also been developed with additional functions that go beyond the concept of filers, for example print servers . However, some of these functions are limited to small networks with a few computers because, depending on the system, special device drivers are required on each connected computer.
Interfaces
The connection to NAS systems is usually established today via Ethernet and TCP / IP . The resulting TCP / IP protocol overhead and bandwidth problems in the past resulted in a somewhat lower suitability for remote mass storage at operating system level, so that SQL servers and similar performance-hungry servers were not installed on NAS-based storage (cf. Storage Area Network ). These restrictions no longer apply to modern NAS agents.
The architecture of NAS enables simultaneous multiple access to data using the corresponding interfaces. Software architectures such as SAP , which require simultaneous multiple access to files, therefore require at least some of the use of NAS implementations. SAN technology cannot guarantee such accesses correctly, which, if not observed, can lead to errors on the consumed file systems.
In particular, NAS systems that are not designed for corporate use but for home or SoHo use can mostly be set up and configured via a web interface .
See also
- Filehosting : a type of network attached storage, which is normally not located in the local network
- Storage Area Network : a network for connecting hard disk subsystems (disk array) and tape libraries to server systems
software
- FreeNAS , XigmaNAS (formerly NAS4Free): Free NAS operating systems based on FreeBSD
- OpenMediaVault : a Debian-based free operating system for NAS
Manufacturer
- Buffalo
- Fujitsu Technology Solutions
- LenovoEMC (formerly Iomega)
- NetApp
- Netgear
- QNAP
- Seagate Technology
- Synology
- Western Digital
Web links
- Network-attached storage background article
- Guide to Building a Secure NAS System Guide
- Definition of NAS. Federal Office for Security in Information Technology
Individual evidence
- ↑ Greg Tomsho: MCSA Guide to Installation, Storage, and Compute with Microsoft Windows Server 2016 . Ed .: Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-337-53283-9 .
- ↑ pcwelt.de
- ↑ Multitalent NAS , c't 20/13, accessed December 11, 2013
- ↑ http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/directnfsclient-11gr1-twp-129785.pdf
- ↑ https://openlab-mu-internal.web.cern.ch/openlab-mu-internal/03_Documents/4_Presentations/Slides/2010-list/2010OOW-08.pdf
- ↑ Archived copy ( memento of the original from July 20, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ http://help.sap.com/saphelp_hanaplatform/helpdata/en/4c/24d332a37b4a3caad3e634f9900a45/frameset.htm
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/305547