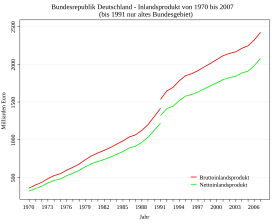
Net domestic product
The net domestic product (NIP) is an economic indicator that shows the material wealth existing in a country .
General
It is the market value of all goods and services that are available to the economic entities involved in domestic production . On average it is about 89% of the gross domestic product .
The net domestic product at factor costs is obtained by subtracting the indirect taxes ( value added tax , tobacco tax, etc.) from the above-mentioned net domestic product at market prices and adding the subsidies .
The net national product at factor cost ( national income ) is obtained by adding to the above-mentioned net domestic product at factor cost the balance of all income from work and property between residents and the rest of the world.
calculation
There are two ways of calculating the net domestic product or net national product:
1)
| + Gross domestic product |
| - depreciation |
| = Net domestic product at market prices |
2) a)
| - Indirect taxes |
| + Grants (e.g. subsidies) |
| = Net domestic product at factor cost |
2 B)
| + Entrepreneurial income |
| + Non-business income |
| = Net national product at factor costs |