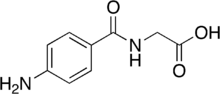
PAH clearance
The PAH clearance ( C PAH ; short for para-aminohippuric acid clearance or p -Aminohippursäure clearance ) is a medical parameter for the assessment of renal function. It describes the volume of blood plasma that the kidneys liberate from para-aminohippuric acid (PAH) by excretion per unit of time . The PAH clearance is used to determine renal blood flow and is therefore used to assess kidney function. The PAH clearance is usually around 550 to 720 ml / min / 1.73 m². Since this method of determining renal clearance is quite complex, it is only used for scientific questions. Today the MAG3 clearance (mercaptoacetyltriglycine) is used, see also kidney scintigraphy .
Execution and calculation
p -Aminohippuric acid is infused as the sodium salt . At low plasma concentrations, the substance is almost completely excreted into the urine during a passage of the blood through the kidneys. This is accomplished by glomerular filtration (20-30%) and tubular secretion (70%) ,
where U PAH and P PAH are the p -aminohippuric acid concentrations in urine and blood plasma, and V is the urinary time volume . Since approximately 90% of p -aminohippuric acid is excreted by the kidneys in the urine, the PAH clearance must be divided by 0.9 to calculate the renal plasma flow (RPF). Taking into account the hematocrit (Hct), the renal blood flow can be calculated from the renal plasma flow: RBF = RPF / (1-Hkt).
Individual evidence
- ^ Klaus Dörner: Clinical chemistry and hematology . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-13-129716-6 .
- ^ Rainer Klinke: Physiology. 6th edition. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2010, ISBN 978-3-13-796006-5 , p. 337.
literature
- BD Rose, TW Post: Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders. 5th edition. McGraw-Hill, New York 2001.