Wedge-headed smooth-forehead caiman
| Wedge-headed smooth-forehead caiman | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Wedge-headed caiman young animal |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Paleosuchus trigonatus | ||||||||||||
| ( Schneider , 1801) |
The wedge-headed smooth-fronted caiman ( Paleosuchus trigonatus ) is a member of the alligator family .
features
The wedge-headed smooth-fronted caiman reaches a maximum body length of about 1.70 meters for the males and about 1.40 meters for the females. Like the only other representative of the smooth-forehead caiman (genus Paleosuchus ), the brow-smooth-forehead caiman ( Paleosuchus palpebrosus ), it is a very small representative of the crocodiles. Its tail is also relatively short. The legs, on the other hand, are relatively long and allow the animals to walk very high, reminiscent of that of mammals . The snout is quite wide and resembles the young crocodile caiman ( Caiman crocodilus ). The neck shields and the shields of the tail are large and triangular, the edges very sharp. Unlike the tails of other crocodiles, that of these animals is not flattened laterally, but dorsoventrally and the double row of shields on the tail protrudes to the side. Other features of the smooth-fronted caimans are the brown eyes and the lack of a bony ridge between the eyes, hence the name of the group. Overall, the body and also the tail are very ossified.
distribution

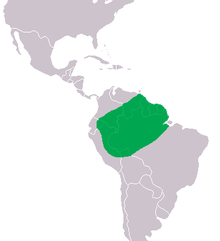
The wedge-headed smooth-forehead caiman lives in the dense rainforests of the Amazon and Orinoco basins . It can be found in Guyana , Suriname and French Guiana , where it is mainly found in the small streams and rivers of the systems. They also regularly hide outside of the water in the undergrowth or in hollow tree trunks.
Way of life
Wedge-headed, smooth-fronted caimans build mounds of soil and plant material that they hide in the undergrowth. The nests are created at the end of the dry season and the females lay between 10 and 15 eggs in them. At the beginning of the rainy season, the young hatch. The adult animals form territories that comprise about 500 to 1500 meters of river. Females reach sexual maturity at around 1.30 meters and males at 1.40 meters, before they do not defend their territories.
The young animals mainly feed on insects , but from a relatively small size they also hunt snakes , birds and lizards . Adult caimans also feed on mammals such as porcupines and pakas .
literature
- Charles A. Ross (Ed.): Crocodiles and Alligators - Development, Biology and Distribution , Orbis Verlag Niedernhausen 2002
- Joachim Brock: Crocodiles - A life with armored lizards , Natur und Tier Verlag Münster 1998
Web links
- Paleosuchus trigonatus in The Reptile Database
- Paleosuchus trigonatus inthe IUCN 2013 Red List of Threatened Species . Listed by: Crocodile Specialist Group, 1996. Retrieved January 30, 2014.