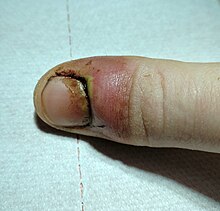
Paronychia
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| L03.0 | Phlegmon on fingers and toes paronychia |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
In medical jargon, inflammation of the nail wall is called (par) onychia , nail bed inflammation or circulation . Various pathogens are possible causes . They are usually preceded by an - often very small - injury to the nail bed, e.g. B. by an excessively shortened or ingrown nail through which germs can penetrate.
Most commonly infection is staphylococcus ago. When the infection migrates into the depths - but much less often than on the flexor side - a panaritium can develop. Treatment consists of relieving the infection and removing the pus responsible for the tenderness. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory pull ointment can be used for this. This can ensure complete healing even in the case of advanced inflammation including granulation . Supplementary baths with curd soap promote healing, as does not wearing sturdy shoes, as sweat and pressure promote inflammation.
Doctors often make an incision for pus accumulation and granulation on toes . However, not only is the tissue cut through to allow the pus to drain away, but parts of the nail bed are also removed and smoothed, which prevents re-growth. The appearance of the affected toe changes significantly (see also Panaritium ).
A colonization of the nail wall with Candida can be the cause. Treatment is then carried out with antifungal drugs .
A syphilitic primary effect can also give the appearance of paronychia.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ nail bed inflammation - zugsalbe-effect.de . In: zugsalbe-effect.de . ( zugsalbe-effect.de [accessed on August 3, 2017]).