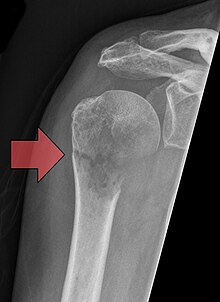
Pathological fracture
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| M84.4 | Pathological fracture, not elsewhere classified |
| M80.- | Osteoporosis with a pathological fracture |
| M90.7 * | Bone fracture in neoplasms (C00-D48 †) |
| M48.5 | Vertebral Compression, not elsewhere classified |
| M49.5 * | Vertebral compression in diseases classified elsewhere |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The pathological fracture ( syn .: Spontaneous fracture ) is a bone fracture that occurs "spontaneously", that is, without adequate trauma , due to a weakening of the bone caused by the disease . The weakened bone structure can break through pulling the muscles during everyday movements as well as through minor trauma (which a healthy bone would have withstood without further ado).
Examples of diseases that are the basis of pathological fractures are osteoporosis or metastases in bones, and more rarely bone tumors (e.g. osteoma , osteosarcoma, etc.), hyperparathyroidism , osteopetrosis , osteomalacia and osteolyses caused by plasmocytoma .
Individual evidence
- ↑ J. Freyschmidt: skeletal disorders: Clinical and radiological diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Springer, 2008, ISBN 978-3-540-45529-5 , p. 49 ff., Limited preview in the Google book search
Web links
Commons : Pathological fracture - collection of images, videos and audio files