Pentode
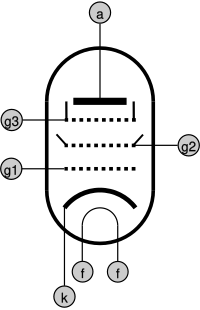
A pentode is an electron tube with five electrodes .
History and characteristics
The pentode (five-pole tube) was invented in 1926 by Bernard Tellegen , an employee at the Philips research laboratory , and patented together with Gilles Holst .
In addition to the anode and cathode , the control grid and the screen grid of the tetrode , it has a cathode connected to the suppressor grid . This keeps the secondary emission of the anode away from the screen grid.
The flat characteristic curve of pentodes shows that the anode is shielded by the additional grid in such a way that a change in the anode voltage hardly has any influence on the anode current. It only depends on the grid pre-tension on the control grid:
triode characteristic curve
This results in a much higher gain.
The beam pentode , which for licensing reasons was called the beam power tetrode , behaves in a similar way .
Examples
Disassembled EL84 v. l. right: cathode, control grid, screen grid, brake grid, anode
Subminiature tubes ECG 5639