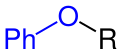
Phenoxy group
| Examples (phenoxy group marked in blue ) |
 phenol |
 any substituted phenol |
 Phenolate anion |
 Phenoxy radical |
 Methoxybenzene |
The phenoxy group is an arrangement of atoms in organic chemistry that adds a heteroatom (oxygen) outside the ring to a benzene ring. The phenoxy group can also be substituted and is then called aryloxy group .
The formula of the substituent is -O-C 6 H 5 and is sometimes abbreviated as -OPh or -OAr. The general abbreviation –OAr can also conceal analogous aromatic groups (e.g. 1-naphthyl instead of phenyl).
The phenoxy group is not an independent substance, but part of a larger molecule (see examples on the right). The smallest molecule in this group is phenol . If the bond between the oxygen and the organyl radical R is split homolytically , the phenoxyl radical is formed (• O – C 6 H 5 ); at a heterolytic cleavage of the hydroxy group of the phenol, a phenolate-anion and a forming proton .
Spellings of the phenoxy group
literature
- Entry on phenoxy. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 3, 2020.