Planarity
Planarity or planicity denotes the spatial arrangement (ie in three-dimensional space) of points in a plane ; the points are then flat (in mathematics: complanar ).
Two plane surfaces that are parallel are called plane-parallel .
Explanation of terms plan - planar
In German usage, it says plan , never planar , as in English, from which it is borrowed in some expressions such as screens, lenses ( Gaussian double lens or planar lens ) or other optical equipment. The term plan means “in a surface”, planar stands for “flattenable” in graph theory ( planar graph ), and for “in the (low) level (flat landscape)” in the geosciences ( lowland level ).
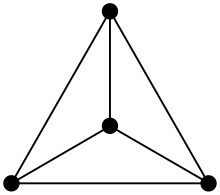
Planarity of graphs
A graph is planar if it can be drawn in a plane in such a way that all edges represented by Jordan curves only intersect at the end points / nodes.
- According to Wagner and Fáry's theorem, there is a straight-line embedding for every planar graph.
- The bounding edges of a graph are called borders.
- Two embeddings are equivalent if there is an isomorphic map between the boundaries of their domains.
- The planarity can be determined algorithmically in linear time.
- If you want to color neighboring nodes of a planar graph differently, you can do this with only 4 colors according to the four-color theorem .
measuring technology
- Planarity describes the surface quality; see flatness in general and surface roughness for special accuracy
- A surface in construction is flat when it is sufficiently flat; see leveling
- Straightening is a production process for shaping a workpiece flat.
optics
With optical lenses, planarity is a quality feature of the extent to which the cut approximates the ideal curve. The expression plane surface is used for the flat surfaces of prisms, lenses or mirrors .
A plane-parallel glass body is called a plane plate .
See also: evenness (technology)