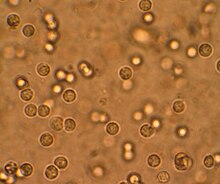
Pyuria
As pyuria ( "Eiterharnen" of gr. Πύον "pus" ούρον "urine") a recognizable with the naked eye admixture is of pus in the urine , respectively. Milky, flaky additions in the urine and a streaky cloudiness are typical.
Microscopically, there are at least 10 leukocytes per mm³ uncentrifuged urine. The cause is mostly bacterial infectious diseases of the urinary organs , i.e. urinary tract infections in the broadest sense. Occasionally, purulent inflammation of the surrounding organs can also be the cause if there is a fistula to the urinary tract. Sterile pyuria is an indication of urogenital tuberculosis .
literature
- Eberhard Aulbert et al .: Textbook of Palliative Medicine . Schattauer Verlag, 2nd edition 2007, ISBN 9783794523610 , p. 463.