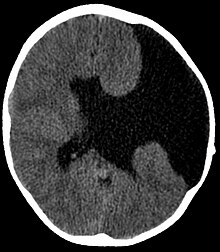
Schizencephaly
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| Q04.6 | Congenital brain cysts |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The term Schizencephaly a rare is cortical malformation of the brain based on a homeobox - gene mutation ( EMX2 understood). It belongs to the group of malformations of the central nervous system .
root cause
The cause could be proven that there was a failure of a transcription factor responsible for the proliferation of the precursor of the neurons in the area of the cerebral cortex . This creates gaps of varying degrees between the two halves of the cerebrum ( cerebral hemispheres ) during the prenatal (prenatal) development of the child . If these malformations are bilateral (on both sides), a connection ( communication ) between the cerebral ventricles can occur.
diagnosis
The diagnosis can be made postpartum using ultrasound , and magnetic resonance imaging can be helpful to check for other gyration disorders .
Effects
It is possible that there are no particular abnormalities in the clinical picture , there are mild forms and severe and extremely severe developmental disorders can occur. This can be accompanied by spastic quadriplegia and epilepsy , especially in the most severe schizencephaly .
Children with the most severe malformations often have a comparatively low life expectancy .
Schizencephaly occurs in about 5 in 10 children with septo-optical dysplasia ( De Morsier syndrome ) and in about 7 in 10 children with Dandy Walker malformation .
Frequency and inheritance
Only a few case studies have been documented so far. Orphanet rates the incidence as 1–9 in 100,000. The majority can be classified as sporadic, with two brothers the peculiarity has also been described. The inheritance is autosomal dominant or recessive, the gene location is 10q26.1. Allelia can be of different severity.
literature
- Deeg, KH: Sonographic diagnosis of cerebral malformations. Migration disorders: lissencephaly, schizencephaly and hemimegalencephaly.
Individual evidence
- ^ Orphanet entry Schizencephaly
- ^ Schizencephaly. In: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man . (English).
Web links
- Clinical manifestations of schizencephaly and their sonographic diagnosis. In: Ultrasound in Medicine. 20, pp. 263-267, doi : 10.1055 / s-1999-8917 .
- J. Froelich, R. Sassen, CE Elger, G. Lehmkuhl: Gelastic Fits in a Two Years Old Boy with a Complex Cerebral Malformation. In: Clinical Pediatrics. 215, 2003, pp. 65-68, doi : 10.1055 / s-2003-38502 .