Mongoose
| Mongoose | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Plain mongoose ( Salanoia concolor ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Salanoia concolor | ||||||||||||
| ( I. Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire , 1837) |
The brown-tailed mongoose ( Salanoia concolor ) is a predatory species from the family of Malagasy carnivores (Eupleridae).
features
Like all Madagascar mongooses, plain mongooses have an elongated, slender body with short limbs. The skull is flattened, the muzzle elongated, and the ears rounded and short. The fur of these animals is dark brown on the upper side and reddish brown on the belly, in contrast to other Madagascar mongooses there are no stripes, and the tail is also a solid dark brown. Plain mongoose reach a head body length of 35 to 38 centimeters, the bushy tail is 16 to 20 centimeters long and the weight is 550 to 780 grams.
Distribution and way of life
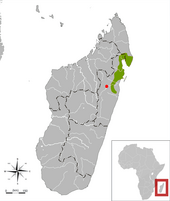
Plain mongooses are endemic to Madagascar . Their habitat are rainforests in the northeast of the island, for example on the Masoala peninsula . They occur primarily between 300 and 700 meters above sea level, occasionally up to 1000 meters.
Little is known about the way these animals live. They are diurnal and especially active in the early morning and late evening. At night they hide in tree hollows or in earthworks. They probably live solitary or in pairs; observations of larger groups are likely to have been a pair of parents with their offspring. It is estimated that a family group lives in an area of around 20 hectares.
Their diet consists mainly of insects, such as beetle larvae. When looking for food, they sometimes climb up to 10 meters high in the trees.
The mating takes place between August and October, after a gestation period of 74 to 90 days, the female gives birth to a single young. This will probably stay with his parents for a year after the birth.
Danger
Due to the destruction of its habitat, the species is listed as "endangered" ( vulnerable ) by the IUCN . There is no evidence of hunting or stalking by introduced predators, but these factors could also pose a threat.
literature
- Ronald M. Nowak: Walker's Mammals of the World . Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore 1999, ISBN 0-8018-5789-9 .
- Don E. Wilson, Russell A. Mittermeier (Eds.): Handbook of the Mammals of the World. Volume 1: Carnivores. Lynx Edicions, 2009, ISBN 978-84-96553-49-1 .
- Nick Garbutt: Mammals of Madagascar. A Complete Guide. Yale University Press, New Haven & London 2007, ISBN 978-0-300-12550-4
Web links
- Salanoia concolor onthe IUCN Red List of Threatened Species . Retrieved on June 17, 2009.